An IT security audit checklist is essential for evaluating vulnerabilities, enforcing security controls, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. It provides a structured approach to assessing IT infrastructure, identifying risks, and strengthening cybersecurity defenses. Without a clear audit process, organizations may face data breaches, compliance violations, and operational disruptions.
A well-structured audit covers risk management, access control, network security, data protection, and regulatory compliance. Systematic review of these areas allows businesses to detect security gaps before attackers exploit them and implement proactive defense strategies. Regular audits help organizations align with security best practices and continuously improve their security posture.
Using an IT security audit checklist streamlines security assessments and ensures critical areas are not overlooked. This guide will provide a step-by-step approach to conducting an effective security audit, equipping organizations with the best practices and tools to stay secure in 2025.
Table of Contents
What is an IT Security Audit?
An IT security audit is a systematic evaluation of an organization’s IT infrastructure, security controls, and policies. It identifies vulnerabilities and potential threats and safeguards systems, networks, and data against unauthorized access, cyber attacks, and compliance violations.
Besides detecting security vulnerabilities, IT security audits also help businesses align with security standards, such as ISO 27001, PCI-DSS, and HIPAA, and reduce legal and financial risks. These audits enable organizations to mitigate threats and enhance their cybersecurity posture proactively through continuous monitoring and security assessments.
Regular security audits are an essential part of a comprehensive security strategy. By reviewing and updating security policies, organizations can adapt to evolving cyber threats and ensure ongoing compliance. A well-structured audit helps strengthen security controls, reinforce data protection measures, and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
Why Do You Need an IT Security Audit?
An IT security audit is vital for protecting sensitive data, complying with regulations, and mitigating cybersecurity threats. It assists businesses in finding weaknesses, strengthening security controls, and preventing the risk of data breaches. Regular audits also support business continuity by ensuring your disaster recovery and incident response plans are working.
Below are the 10 reasons highlighting the importance of an IT security audit for your organization.
- Protect sensitive data to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Ensure compliance with PCI DSS, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and other regulations to avoid legal penalties.
- Identify and mitigate cybersecurity risks before they become threats, ensuring proactive defense.
- Reinforce disaster recovery and business continuity plans to minimize downtime in case of an attack.
- Reduce financial and reputational damage by preventing costly security incidents.
- Prevent unauthorized access by enforcing strict access control policies and authentication measures.
- Improve network security by detecting firewall misconfigurations and closing potential attack vectors.
- Enhance employee security awareness through periodic training to reduce human errors and phishing risks.
- Support third-party risk management by ensuring vendors meet security compliance standards.
- Offer actionable insights to refine and strengthen the organization’s cybersecurity strategy continuously.
Types of IT Security Audits
There are three types of IT security audits: internal, external, and compliance-based audits. Their goal is to asses an organization’s security posture, identify vulnerabilities, and maintain industry-specific compliance. A combination of these security audits facilitates a comprehensive security assessment, ensuring organizations bolster their defenses against cyber threats.

- Internal Security Audit
Carried out by the organization’s IT team or an internal audit department, an internal security audit asses an organization’s internal security controls and policies. Through self-assessment, this method helps identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and access control weaknesses before external audits or attacks occur.
This audit includes security aspects such as network security, access controls, data protection, and incident response. Although this cost-effective method detects security gaps early and helps maintain ongoing security improvements, the lack of objectivity and expertise in advanced threat detection can be challenging.
- External Security Audit
For an external security audit, the organization seeks independent third-party cybersecurity firms or regulatory bodies to provide an unbiased assessment of its security infrastructure and regulatory compliance. This method validates security measures against industry best practices through penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and security policy reviews.
An external security audit helps businesses detect security gaps overlooked by internal teams and ensure compliance with ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, and other standards. Despite these benefits, this audit can be expensive and requires significant preparation to maintain compliance.
- Compliance-Based Audits
By assessing an organization’s adherence to legal, regulatory, and industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, and NIST Cybersecurity Framework, compliance-based audits guarantee that the organization avoids legal and financial penalties. The main objective of this audit is to align the data protection policies, security controls, and risk management procedures with mandated security frameworks.
Compliance-based audits often require periodic and ongoing checks to ensure adherence to legal mandates. This helps improve trust with customers and stakeholders and maintain business integrity. However, the only downside is that they are time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Key Components of an IT Security Audit Checklist
An IT security audit checklist is essential for identifying vulnerabilities, enforcing security policies, and maintaining compliance in critical security areas. The checklist covers risk assessment, access control, network security, data protection, and regulatory requirements, enabling organizations to protect sensitive information and safeguard against cyber threats.

The necessary components included in an IT security audit checklist are discussed below.
- Risk Assessment & Threat Analysis
Conducting a thorough risk assessment helps organizations detect and mitigate potential security threats before they impact the IT infrastructure. The audit should focus on:
- Identifying vulnerabilities and security risks: Review the security system for misconfigured settings, outdated software, and lack of security patches.
- Evaluating threat vectors and attack surfaces: Analyze common cyber threats such as phishing attacks, insider threats, and malware infections to determine their potential impact on business operations.
- Conducting a threat modeling process: Predicts potential attack scenarios and strengthens defenses against the identified risks.
- Access Control & Identity Management
Reviewing user access control and permissions ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information and resources. This involves:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Restrict unauthorized logins and credential theft.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Enforce access restrictions based on job responsibilities to minimize excessive permissions.
- Privileged account management (PAM): Control and monitor access for admin users and accounts to safeguard against cyberattacks, comply with regulations, and improve operational efficiency.
- Network & Infrastructure Security
A secure network infrastructure protects organizations against cyber intrusions and unauthorized access. The security audit should assess:
- Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS): Review firewall rules, configurations, and the effectiveness of IDS in detecting threats.
- VPNs and encrypted communication protocols: Ensure remote access through TLS, IPSec, and SSL VPNs.
- Network segmentation: Evaluate how critical systems are isolated to prevent lateral movement by attackers.
- Remote access security: Audit VPN usage, authentication protocols, and access control measures for remote employees.
- Endpoint Security & Device Protection
Safeguarding endpoints, including laptops, mobile devices, and IoT systems, against malware infections and unauthorized access is essential. The audit should include:
- Antivirus and antimalware solutions: Confirms that endpoint security software is installed and updated on all devices.
- Patch management and software updates: Timely delivery of security patches for all operating systems and applications.
- Mobile device security policies: Reviews encryption, remote wipe capabilities, and app restrictions to protect corporate data.
- Endpoint access control: Verifies that device authentication measures prevent unauthorized access to company networks.
- Data Protection & Encryption Policies
Robust data protection measures ensure that sensitive data are safe from data breaches and meet security standards. The security audit should encompass:
- Encryption standards: Ensure AES-256 for stored data and TLS/SSL protocols for secure communications.
- Backp and disaster recovery strategies: Review backup frequency, off-site storage, and disaster recovery testing.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions: Leverage Forcepoint, Code42, and Digital Guardian DLP for preventing unauthorized access, transfer, and leaks.
- Access control: Verify and manage access to critical business and customer information to protect sensitive data.
- Security Awareness Training & Incident Response
Providing security awareness training to employees and preparing an effective incident response plan becomes crucial for preventing cyber threats. The audit should examine:
- Employee security training programs: Provide regular training sessions on phishing threats, password security, and social engineering.
- Phishing simulation tests: Train staff and evaluate their response to simulated cyberattacks to gauge security awareness
- Incident response plan effectiveness: Review the organization’s ability to detect, contain, and recover from security incidents.
- Security drill execution: Regularly conduct cyberattack simulations to refine response strategies.
- Compliance & Regulatory Requirements
Adherence to industry-specific regulations safeguard sensitive data and avoid legal fines. The adult should cover:
- Regulatory compliance verification: Maintain compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DS, and ISO 270001 standards.
- Audit logs and security documentation reviews: Ensure proper management of system logs and compliance reports.
- Cyber insurance coverage: Assesses insurance policies for data breach response and liability protection.
How to Conduct an IT Security Audit?
Conducting an effective IT security audit requires defining the audit scope, assessing risk, implementing a review, identifying vulnerabilities, testing security controls, and documenting the findings into a detailed report.
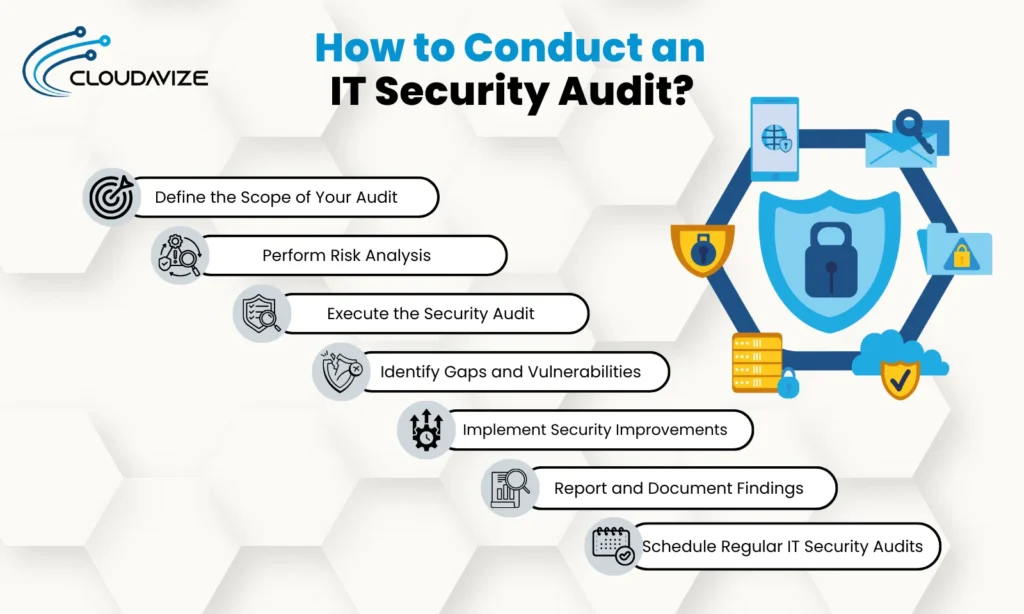
Below is a step-by-step guide providing thorough knowledge required to conduct an IT security audit
Step 1: Define the Scope of Your Audit
The IT security audit process starts by identifying the assets and systems that need to be audited, including servers, databases, applications, and endpoints. Determining regulatory and compliance requirements such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS validates legal adherence. By clearly defining the audit scope, organizations can prioritize critical areas and consider all security gaps. This helps verify the audit objectives and assign responsibilities to the right personnel.
Step 2: Perform Risk Analysis
The second step involves assessing potential security risks by evaluating threat vectors (hackers, insiders, malware) and attack surfaces. Prioritizing risks based on their frequency and consequences helps focus on critical vulnerabilities that are highly likely to lead to data breaches and system failures. Developing a well-structured risk analysis allows for the effective allocation of resources while mitigating high-risk security threats.
Step 3: Execute the Security Audit
Organizations should choose between the internal security team or external auditors for an unbiased security audit. The selected choice should conduct a systematic review of system configurations, security logs, and access control policies. Executing the security audit thoroughly using vulnerability scanning, and penetration testing helps detect unauthorized access points, outdated software, and potential weak points before attackers can exploit them.
Step 4: Identify Gaps and Vulnerabilities
Once the audit findings are collected, it is time to analyze the security gaps. Auditors should use security audit tools to scan misconfigurations, outdated software, and potential threats. They also perform penetration testing to evaluate security controls for prevention of unauthorized access. This step also involves comparing current security posture against best practices and categorizing gaps based on their severity. Through these activities, organizations can generate a vulnerability report that helps determine potential exploitability of vulnerabilities.
Step 5: Implement Security Improvements
After identifying security gaps, auditors address them by patching vulnerabilities, updating policies, strengthening access controls, improving incident response mechanisms, and facilitating security awareness training. Incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA), encryption, and threat monitoring measures enhances cybersecurity frameworks. Implementing improved security measures reduces the risk of exploitation and solidifies the overall security posture.
Step 6: Report and Document Findings
The next step involves documenting the findings of the entire auditing process and creating a detailed report. The report should include the audit objectives and scope, identified risks, security gaps, compliance status, recommended security measures, remediation actions, and suggested improvements for future audits. Creating comprehensive documentation empowers management and stakeholders to make informed decision, and draft an effective security plan, ensuring long-term protection.
Step 7: Schedule Regular IT Security Audits
The final step is to establish a security audit schedule based on quarterly or annual requirements. This requires implementing continuous monitoring with SIEM solutions and threat detection systems to address emerging issues proactively. Automating compliance checks using security tools and outsourcing auditing to third-party vendors for independent validation also confirms continuous security improvement. Regular audits create a culture of proactive security in the organization, ensuring resolution of evolving threats before they become critical issues.
IT Security Audit Tools to Consider
Using the right IT security audit tools ensures proper vulnerability detection, risk assessment, and adherence to industry standards. Implementing these tools helps organizations proactively detect threats, fortify cybersecurity defenses, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Below are key security audit tools based on their functionality
- Security Assessment Platforms: Help identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and security flaws in IT infrastructure. (Nessus, Qualys,Bup Site, Nmap, Rapid7)
- Compliance and Risk Management Software: Uphold regulatory compliance with ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI-DSS. (IBM OpenPages, AudtBoard, SAP GRC, Navex RiskRate)
- Endpoint Security Tools: Detects and prevents malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. (CrowdStrike Falcon, Splunk, Sophos Intercept X, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint)
When Should You Perform an IT Security Audit?
You should perform an IT security audit quarterly or annually. It should also be conducted after a security breach or incident and when renewing compliance certifications. The frequency of IT security depends on the needs of the business, regulatory requirements, and emerging cybersecurity threats.
Here are the 3 key scenarios when an IT security audit should be performed
- Periodic Audits – Organizations should schedule quarterly or annual IT security audits to proactively detect security gaps, assess risk levels, and update security policies. Conducting regular audits helps evaluate network security, review access controls, and ensure compliance.
- After a Security Breach or Incident – An immediate IT security audit is necessary after a data breach, ransomware attack, or unauthorized access so organizations can identify the vulnerabilities that led to the audit. It also helps assess the extent of damage and contain threats, paving the path to strengthening security defenses to prevent future attacks.
- Compliance Renewal Requirements – Businesses must maintain certifications and regulatory compliance to avoid fines and maintain operational continuity. Therefore, conducting an IT security audit while renewing compliance with SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA, and other security frameworks becomes necessary to mitigate data protection risks.
How does Cloudavize Help with your IT security audit?
Conducting an IT security audit requires risk assessment, compliance tracking, and continuous monitoring to protect critical systems. Manual audits can be time-consuming and prone to errors, making automation essential.
Cloudavize simplifies IT security audits by offering automated compliance reporting, real-time monitoring, and proactive risk mitigation. It helps businesses stay compliant, detect security gaps, and elevate cyber posture without manual complexities.
With continuous monitoring, Cloudavize identifies threats in real time, reducing security risks. It’s automated reporting streamlines audit preparation, ensuring a secure and compliant IT environment. Integrating Cloudavize into your security strategy enhances audit efficiency and overall cybersecurity.
FAQs About IT Security Audits
What are common security audit mistakes?
Some of the common mistakes that occur during a security audit are:
- Ignoring small security gaps.
- Not updating security policies.
- Failure to test and review access controls.
How long does an IT security audit take?
The timeframe for an IT security audit varies depending on the organization and the complexity of the IT system. Small businesses (SMBs) take a couple of weeks to complete, while large enterprises take over 4 weeks.
What is the difference between an IT audit and a cybersecurity audit?
An IT audit evaluates an organization’s IT infrastructure, policies, and operational efficiency, while a cybersecurity audit focuses on security risks, vulnerabilities, and threat migration strategies.
Can a security audit guarantee complete protection?
No, a security audit cannot guarantee complete protection. However, it helps reduce risks by identifying vulnerabilities before cybercriminals can exploit them. It also strengthens defenses through regular risk assessments and policy updates.




