In a world where technology powers every business operation, even a brief system outage can disrupt services, cause financial loss, and damage customer trust. To manage these risks, organizations must create a clearly defined IT Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP). A DRP outlines the steps required to restore IT systems, data, and networks following an unexpected incident.
As cyber threats, natural disasters, and critical system failures continue to grow in frequency and impact, the importance of having a structured recovery checklist becomes more urgent. Without a clear plan, recovery efforts can become chaotic, delayed, or incomplete, leading to even greater disruption. A checklist brings clarity and direction to your recovery process.
This blog presents a 10-step IT Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist that helps organizations prepare for, respond to, and recover from IT disruptions. From setting recovery goals and assessing risk to establishing failover infrastructure and conducting regular tests, each step supports operational resilience and security.
Whether your goal is to build a new DRP or optimize an existing one, this guide covers all essential elements such as data backup procedures, incident response, compliance requirements, and continuous improvement. Use this checklist to ensure your organization is prepared to recover quickly and maintain continuity in the face of disaster.
Table of Contents
What is an IT Disaster Recovery Plan?
An IT disaster recovery plan is a detailed document that indicates how an organization responds and restores IT systems and infrastructure during and after an unplanned incident for business continuity. Common unplanned incidents impacting the IT environment include cyberattacks, such as ransomware, DDoS attacks, and data breaches, hardware failures and data corruption, natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, or wildfires, and power outages and network failures.
The primary purpose of an IT disaster recovery plan is to help organizations prevent data loss by backing up critical data and information in the cloud in multiple servers across different locations instead of on-site physical hardware. This approach allows businesses to swiftly recover lost data, helping minimize downtime and ensure continuous business operations.
The two pillars of IT DRP are the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) which set guidelines for restoring business operations with minimal disruption. They form the foundation of an organization’s disaster recovery strategy that aligns with the overall business continuity plan.
To ensure the IT DRP is executed effectively, organizations rely on a detailed IT Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist that outlines the necessary tasks and procedures necessary to prepare, respond to, and recover from an IT disaster.
Why is an IT Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist Important?
An IT disaster recovery plan checklist is essential to provide a systematic roadmap toward critical recovery tasks with minimal errors and downtime during natural or man-made disasters. Following the action plan thoroughly helps in the quick recovery and restoration of the affected systems, reducing downtime, minimizing data loss, and avoiding operational paralysis.
Below are the 8 key points highlighting the importance of using an IT disaster recovery plan checklist.
- Reduces downtime by outlining step-by-step recovery procedures.
- Protects sensitive data through regular, encrypted backups.
- Ensures compliance by aligning with HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001, and NIST frameworks.
- Minimizes financial losses by enabling faster system and service restoration.
- Improves response time by assigning predefined roles and escalation paths.
- Clarifies team responsibilities with a documented communication plan.
- Supports audit readiness through detailed logs and DRP documentation.
- Strengthens business continuity by integrating IT recovery with organizational workflows.
What are the Steps To Create an IT Disaster Recovery Plan?
The steps to create an IT disaster recovery plan include everything from defining recovery objectives, assessing risks, and assigning responsibilities to creating a disaster recovery site and verifying the effectiveness of DRP for adhering to standard regulations and improving the plan.
This 10-step checklist provides a structured, step-by-step process that ensures the security of critical IT systems to safeguard data, perform reliable data recovery, and maintain operational continuity.
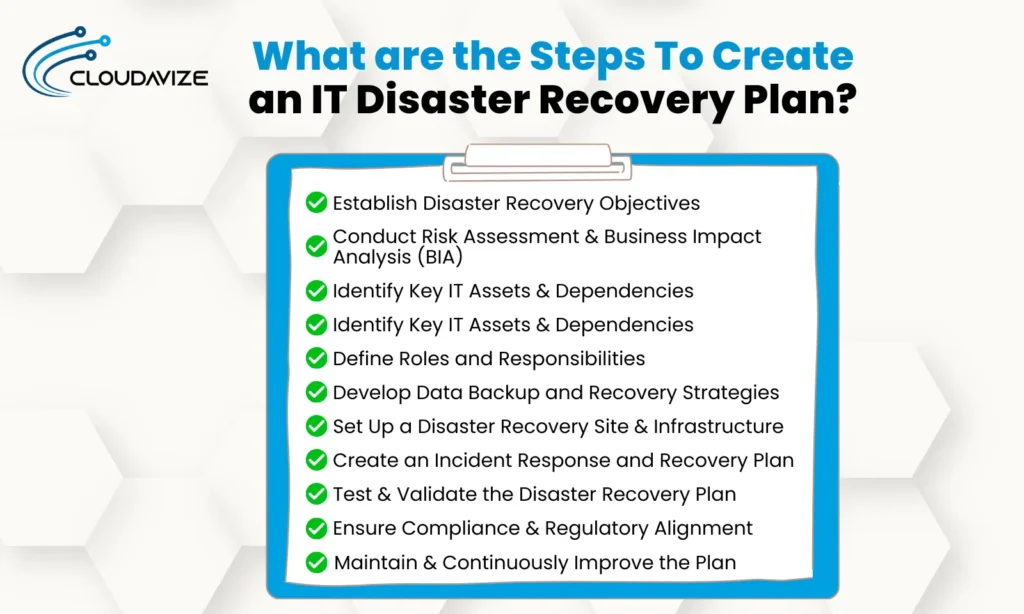
- Establish Disaster Recovery Objectives
The first step requires organizations to define a clear scope and purpose of the DRP to guide all the planning efforts. This includes identifying critical IT infrastructure, applications, and data assets integral to business continuity. Here, organizations should set RTO to define the limit of acceptable downtime and RPO for tolerable data loss. These predefined recovery objectives ensure seamless resilience by aligning recovery goals with the broader business continuity strategy.
- Conduct Risk Assessment & Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Once the recovery objectives are set, organizations must perform a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential threats such as cyberattacks, hardware failures, or natural disasters. Likewise, BIA helps to determine the impacts of these unexpected disruptions in business operations and finances, allowing businesses to assign system priority with minimal consequences. This analysis helps outline the interdependencies between services and infrastructure, enabling companies to know the associated losses from downtime.
- Identify Key IT Assets & Dependencies
Organizations should document all on-premise and cloud-based resources, including servers, databases, applications, networks, and storage devices. This step allows businesses to understand the dependencies between resources so they can recover IT assets based on criticality and urgency. By identifying crucial IT assets and their dependencies, companies can visualize critical paths and avoid bottlenecks during recovery. For its success, implementing redundancy and failover mechanisms for high-priority assets becomes a must.
- Define Roles and Responsibilities
The next step is to form a Disaster Recovery Team (DTR) and assign specific disaster recovery roles and responsibilities to in-house personnel, including IT admins, cybersecurity experts, communication leads, and external vendors. Defines roles help prevent confusion during emergencies and enable faster recovery of IT systems with swift actions. This step also requires proper maintenance of the emergency contact list and communication channels between internal and third-party providers for organized response actions.
- Develop Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
The fifth step is to implement a 3-2-1 backup strategy. It means three data copies, two storage types, and one offsite or cloud-based location. This strategy would be backed up with clear backup schedules and retention policies that update data on time and make it accessible around the clock. Organizations should select the backup and recovery solutions that provide encryption and role-based access control for data integrity and reliability.
- Set Up a Disaster Recovery Site & Infrastructure
Businesses must decide the type of disaster recovery site they require to restore business operations swiftly. Cold site offers low-cost redundancy, Warm site provides faster activation, and Hot site offers real-time synchronization. No matter the choice, disaster recovery sites should be equipped with redundant power, networking, data storage systems, and telecommunications capabilities. Proper configuration of these sites ensures significant downtime reduction during incidents.
- Create an Incident Response and Recovery Plan
After selecting the disaster recovery site, organizations need to draft step-by-step procedures for identifying, containing, and resolving IT incidents, including immediate detection, initial response, failover activation protocols, system shutdown processes, and communication workflows. Companies should provide clear, actionable steps that guide teams through crisis management and ensure the rightful integration of DRP with the existing cybersecurity Incident Response Plan (IRP) for a unified response strategy.
- Test & Validate the Disaster Recovery Plan
To certify the proper working of DRP, tabletop exercises, walkthrough drills, and full-scale simulations replicating the actual disaster scenario must be conducted to evaluate its effectiveness and readiness. These testing and outcomes allow organizations to acknowledge the faults and inconsistencies of the plan so they can refine procedures, close gaps, and improve response speed. They should also include penetration testing to evaluate the plan’s resilience against cybersecurity threats.
- Ensure Compliance & Regulatory Alignment
The next step is to verify whether your disaster recovery plan complies with relevant industry regulations and legal requirements like ISO 27001, NIST, HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC 2. Organizations should include policies to verify that third-party vendors align with your DR requirements. They also need to maintain detailed documentation, audit logs, and test records to demonstrate compliance during reviews. By adhering to regulations, they can mitigate legal risk and enhance stakeholder trust and reliability.
- Maintain & Continuously Improve the Plan
Organizations should routinely review, revise, and improve the disaster recovery plan to reflect changes in technology, business operations, and emerging threats. They should integrate feedback and lessons learned from real incidents, simulated tests, and other recovery exercises to identify areas needing enhancement to strengthen the plan. Monitoring industry trends and adopting advanced disaster recovery technologies ensures that the DRP remains effective and proactive to organizational needs.
What are the Components of an IT Disaster Recovery Plan Checklist?
The components of an IT disaster recovery plan checklist include DRP documentation, Business Impact Analysis (BIA), recovery goals, backup protocols, recovery site, testing, and continuous integration. These building blocks help prepare an effective IT disaster recovery strategy that protects critical assets, restores services quickly, minimizes downtime, and maintains business continuity under adverse conditions.

DRP Documentation and Planning
Effective DRP documentation provides clear, structured guidelines on roles, responsibilities, and recovery procedures. It includes contact lists, asset inventories, and step-by-step strategies for restoring your systems.
- Create a centralized, up-to-date disaster recovery documentation platform.
- Define roles and responsibilities for disaster recovery team members.
- Include contact lists, system inventories, and restoration procedures.
- Maintain clear, step-by-step strategies for system recovery.
Risk Assessment & Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Conducting risk assessments helps businesses identify potential threats, such as cyberattacks, hardware failures, and natural disasters.
- Conduct a Business Impact Analysis to determine the impact of system downtime.
- Prioritize systems based on operational, financial, and reputational impact.
- Use findings to define targeted disaster recovery actions.
Recovery Objectives
Defining the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) helps companies determine their downtime and data loss threshold. These objectives guide how quickly businesses need to get systems back online and how recent the data you recover should be.
- Define the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) for each critical system.
- Set the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) to determine acceptable data loss limits.
- Establish Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with third-party vendors or MSPs.
- Ensure all recovery goals align with business continuity requirements.
Backup and Recovery Procedures
Protecting your organization’s critical data with comprehensive backup and recovery procedures should be at the top of your priority list.
- Define the backup frequency and type (e.g., full, incremental, differential).
- Use secure, encrypted storage solutions (cloud or offsite).
- Document data restoration steps and validation protocols.
- Ensure backup data is regularly tested for integrity and accessibility.
Disaster Recovery Site/Environment
A disaster recovery site, whether hot, warm, or cold, acts as a lifeline when your primary business location is unavailable.
- Ensure the site mirrors production systems, network configurations, and data.
- Regularly update and test recovery site infrastructure.
- Monitor and synchronize the recovery site with live environments.
DRP Testing and Exercises
Regular testing through simulations, drills, and tabletop exercises helps validate the effectiveness of a disaster recovery plan.
- Conduct scheduled tabletop exercises, drills, or live simulations.
- Review test outcomes and document lessons learned.
- Adjust and update the DRP based on testing feedback.
- Train staff regularly to understand roles during recovery scenarios.
Business Continuity Integration
Integrating the DRP with the broader Business continuity plan ensures alignment between OT recovery and overall business resilience.
- Align the IT DRP with the overall Business Continuity Plan (BCP).
- Collaborate with non-IT departments like finance and operations.
- Ensure critical services (e.g., communication, logistics) remain functional.
- Review interdependencies between business units and IT recovery timelines.
Ensure Business Continuity with an IT Disaster Recovery (DR) Checklist
Maintaining business continuity during unexpected disruptions requires a proactive and well-structured IT Disaster Recovery (DR) checklist. Organizations must regularly back up critical data using cloud-based or offsite storage to preserve data integrity during outages. Additionally, implementing failover systems, redundant networks, and backup power solutions minimizes downtime and protects essential operations from IT failures.
Cloudavize, a trusted managed service provider, helps SMBs and enterprises develop, test, and maintain effective DR checklists tailored to their specific needs. By conducting regular simulations, tabletop exercises, and system recovery drills, Cloudavize ensures that your disaster recovery processes remain current, reliable, and fully aligned with business continuity goals.



