An IT audit checklist is a structured tool used to assess an organization’s IT systems, security controls, policies, and compliance with industry standards. It provides a step-by-step framework to evaluate hardware, software, networks, risk management, data protection, and regulatory compliance to ensure IT infrastructure is secure, efficient, and aligned with business objectives.
A well-structured IT audit checklist ensures your business’s IT systems, security policies, and compliance measures are effectively evaluated and optimized. It helps identify vulnerabilities, mitigate cybersecurity risks, and enhance overall IT governance. Whether you want to protect sensitive data, ensure regulatory compliance, or improve system performance, a comprehensive IT audit checklist covers all critical areas, including IT asset inventory, access controls, data backup verification, and adherence to standards like ISO 27001, GDPR, NIST, and PCI-DSS.
Regular IT audits help prevent security breaches, financial losses, and downtime, ensuring your IT environment remains resilient and future-ready. By following a structured audit process, businesses can proactively address risks, enhance IT efficiency, and strengthen security. Engaging certified IT auditors (CISA, CISSP, CRISC) ensures expert guidance, keeping your systems secure, compliant, and optimized for long-term business growth.
Table of Contents
What is an IT Audit and Why is it Important?
An IT audit is a structured assessment of an organization’s IT infrastructure, security protocols, and operational processes to ensure compliance, risk management, and system efficiency. It involves evaluating network security, software integrity, data protection, and IT governance to identify vulnerabilities and enhance overall IT resilience. As businesses increasingly rely on digital systems, IT audits help maintain data integrity, prevent cyber threats, and optimize IT operations. Without regular assessments, organizations risk security breaches, financial losses, and operational inefficiencies due to outdated infrastructure and weak cybersecurity controls.
To mitigate these risks, IT audits play a crucial role in strengthening security, ensuring compliance, and optimizing IT performance. By systematically evaluating IT systems, businesses can identify weaknesses, improve governance, and enhance operational efficiency. Below are the key benefits of conducting regular IT audits.
- Risk Mitigation – IT audits identify cybersecurity threats, system misconfigurations, and unauthorized access points, allowing organizations to implement proactive security controls.
- Regulatory Compliance – Ensuring compliance with global and industry-specific regulations helps businesses avoid fines, legal actions, and reputational damage.
- IT Governance and Accountability – Audits enhance IT governance by reviewing access controls, security policies, and risk management strategies, ensuring accountability and alignment with best practices.
- Operational Efficiency – Evaluating hardware performance, software effectiveness, and system workflows helps organizations eliminate inefficiencies, optimize resource allocation, and improve productivity.
- Financial Security – IT audits prevent financial fraud by detecting inefficient IT spending, unauthorized transactions, and security gaps.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery – Regular audits verify data backup integrity, incident response plans, and disaster recovery strategies, ensuring that businesses can recover IT operations quickly after cyber incidents.
- Cloud and Data Security – As businesses migrate to cloud-based infrastructures, IT audits evaluate cloud security configurations, third-party vendor risks, and identity management controls to ensure data integrity and compliance.
What Are the Key Components of an IT Audit Checklist?
A structured IT audit checklist ensures a comprehensive review of an organization’s IT management, security, and compliance. By evaluating infrastructure, security controls, operations, data management, and cloud services, auditors can identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and optimize IT governance. The following key components form the foundation of an effective IT audit checklist.

IT Infrastructure
A robust IT infrastructure is essential for system stability, security, and operational efficiency. The audit should focus on:
- Hardware and Software Inventory Assessment – Identifies all IT assets, ensuring proper tracking, licensing, and maintenance to prevent unauthorized or outdated systems from introducing security risks.
- Network Architecture and Segmentation Review – Evaluates the design, efficiency, and security of network infrastructure, ensuring segmentation policies protect critical data and systems from cyber threats.
- IT Asset Lifecycle Management – Examines the procurement, deployment, maintenance, and decommissioning of IT assets to ensure cost efficiency and security compliance.
IT Security
IT security audits help safeguard sensitive data and critical systems against cyber threats. Key areas include:
- Risk Management and Cybersecurity Protocols – Reviews vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and risk mitigation strategies to protect against malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access.
- Ensuring Compliance with Regulatory Standards – Verifies adherence to ISO 27001, COBIT, NIST, PCI-DSS, and GDPR, ensuring that security measures align with industry regulations.
- IT Security Audit Checklist – Evaluates firewalls, encryption, endpoint security, and access control mechanisms to prevent data breaches and insider threats.
IT Operations and Support
Efficient IT operations are critical for business continuity and service reliability. Audits should cover:
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Practices – Assesses incident management, service requests, and change management frameworks to enhance IT service delivery and support efficiency.
- Incident Response and Helpdesk Procedures – Reviews response times, issue resolution processes, and escalation protocols to ensure IT teams can quickly address security incidents and technical disruptions.
- Change Management and IT Continuity Planning – Evaluates documentation, approval workflows, and testing procedures for system updates, software patches, and infrastructure changes to prevent unintended downtime.
Data Management
Data is a critical business asset, and IT audits must verify protection, recovery, and business continuity strategies. Key areas include:
- Backup Frequency and Validation – Ensures that regular, automated backups are conducted and tested for data integrity and rapid recovery.
- Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) Essentials – Reviews recovery objectives, failover mechanisms, and testing protocols to ensure minimal downtime during a system failure or cyberattack.
- Business Continuity Planning – Assesses data redundancy, emergency response procedures, and alternative access strategies to maintain operations during IT disruptions.
Cloud Services
With growing cloud adoption, IT audits must address cloud security, vendor management, and identity governance. The checklist should include:
- Cloud Security Configurations and Compliance – Evaluates encryption standards, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and cloud access policies to protect sensitive data stored in AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Vendor Management and Third-Party Risk Assessment – Assesses service-level agreements (SLAs), security certifications, and compliance measures of cloud providers and third-party vendors.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) in Cloud Environments – Reviews user roles, privilege management, and access monitoring to prevent unauthorized access to cloud resources.
A well-executed IT audit checklist helps organizations maintain security, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency, ensuring that IT systems remain resilient against evolving cyber threats.
What Are the Steps in an IT Audit Process?
A structured IT audit process ensures a thorough evaluation of IT controls, security measures, and compliance requirements. Each step plays a crucial role in identifying risks, assessing system integrity, and strengthening IT governance. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key steps involved in conducting an IT audit.
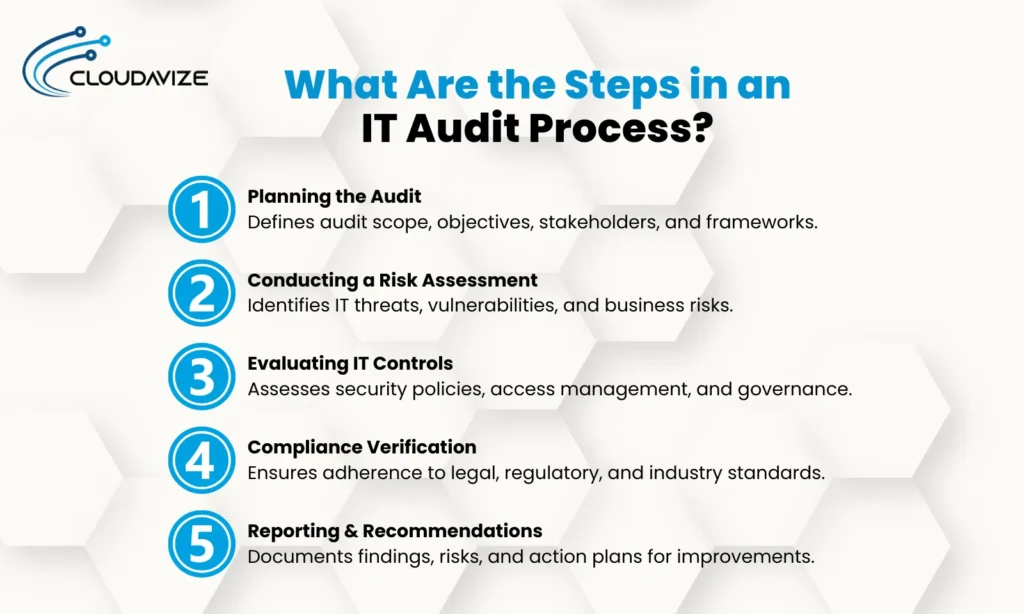
Step 1 – Planning the Audit
The planning phase is critical for defining the audit scope, objectives, and methodology. Auditors work with IT teams, compliance officers, and business stakeholders to identify the systems, processes, and regulations that will be assessed. A risk-based approach is typically used, focusing on high-impact IT assets and vulnerabilities. This phase also includes selecting audit frameworks such as ISO 27001, NIST, COBIT, and ITIL, ensuring alignment with industry standards.
Key Considerations to include:
- Define the audit objectives (e.g., security assessment, regulatory compliance, IT efficiency).
- Determine the audit scope, including IT infrastructure, security policies, and data management.
- Identify key stakeholders, including IT leadership, risk management teams, and compliance officers.
- Select audit criteria and frameworks such as ISO 27001, NIST, SOX, GDPR, or HIPAA.
- Establish the audit methodology, defining tools, techniques, and assessment approaches.
A well-planned audit ensures clarity in objectives, smooth execution, and comprehensive risk coverage, setting the foundation for a successful IT assessment.
Step 2 – Conducting a Risk Assessment
A risk assessment helps identify potential IT threats, vulnerabilities, and business risks. This involves reviewing network security, software vulnerabilities, access control gaps, and potential compliance violations. Auditors analyze the likelihood and impact of each risk, prioritizing areas that require immediate action. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment techniques are used to assign severity levels and establish remediation priorities.
Key Considerations in This Step:
- Identify critical IT risks such as cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and system failures.
- Assess the likelihood and potential impact of each risk on business operations.
- Determine risk tolerance levels and prioritize high-risk areas for further evaluation.
- Develop a risk register, documenting identified vulnerabilities and mitigation strategies.
By conducting a thorough risk assessment, organizations can proactively address security gaps and enhance IT resilience, reducing exposure to operational and financial risks.
Step 3 – Evaluating IT Controls
Once risks are identified, auditors assess the effectiveness of IT controls in place to mitigate them. This includes evaluating security policies, access management protocols, IT governance frameworks, and system monitoring processes. Security tests such as penetration testing and vulnerability scans help identify weaknesses in network security, cloud configurations, and endpoint protection mechanisms.
Key Considerations in This Step:
- Assess internal IT controls, including user authentication, firewall settings, and encryption mechanisms.
- Review IT governance policies, ensuring compliance with security best practices.
- Test incident response protocols and evaluate system monitoring effectiveness.
- Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify exploitable weaknesses.
A strong IT control environment ensures data confidentiality, system integrity, and regulatory compliance, protecting the organization from cyber threats and operational disruptions.
Step 4 – Compliance Verification
Compliance verification ensures that IT systems adhere to legal, regulatory, and industry standards. Auditors review policies related to data protection, security controls, and third-party vendor compliance. They validate documentation, security logs, and system configurations to confirm alignment with SOX, PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulatory frameworks.
Key Considerations in This Step:
- Validate compliance with ISO 27001, NIST, COBIT, GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX.
- Review audit logs, access control mechanisms, and security configurations for compliance.
- Assess third-party vendor contracts, ensuring adherence to security and privacy requirements.
- Ensure audit documentation is complete and available for regulatory review.
By ensuring regulatory compliance, organizations minimize legal risks, avoid penalties, and maintain trust with customers and stakeholders.
Step 5 – Reporting & Recommendations
The final step involves documenting findings, providing recommendations, and outlining an action plan for IT improvements. Audit reports summarize identified risks, compliance gaps, and security weaknesses, along with corrective actions. The report is shared with IT leadership, compliance teams, and executive management to prioritize and implement security enhancements.
Key Considerations in This Step:
- Compile a comprehensive audit report, detailing security risks and compliance issues.
- Provide actionable recommendations to mitigate identified vulnerabilities.
- Develop an implementation roadmap, assigning responsibilities and deadlines for IT improvements.
- Establish follow-up procedures to track remediation progress and verify compliance updates.
A well-structured audit report ensures that IT teams and business leaders have clear insights into IT risks and necessary actions, leading to stronger security, improved compliance, and enhanced IT efficiency.
Best Practices for Using an IT Audit Checklist
An IT audit checklist is essential for systematically assessing IT systems, security, and compliance. Adopting best practices ensures audits are thorough, actionable, and aligned with business objectives, helping organizations identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and maintain compliance. Here’s how to make the most of your IT audit checklist:
1. Clearly Define Audit Objectives
Before conducting an audit, it is crucial to establish clear objectives. Define whether the audit focuses on security, compliance, or IT governance, ensuring it aligns with business goals and regulatory requirements. The checklist should comprehensively cover data security, access controls, and system resilience, helping organizations address potential weaknesses and improve IT performance.
2. Customize the Checklist for Your Organization
Every organization has unique IT needs, so the checklist should be tailored accordingly. It should reflect specific IT environments, industry regulations, and risk factors. Incorporating standards like ISO 27001, NIST, COBIT, and ITIL ensures a structured approach. Prioritizing high-risk areas, such as firewall settings, data backup processes, and access permissions, strengthens security and ensures compliance.
3. Use a Structured Approach
A well-organized audit checklist enhances clarity and effectiveness. Categorizing sections under network security, cloud security, compliance, and risk management ensures comprehensive coverage. Every checklist item should be actionable, measurable, and verifiable, making it easier to track progress. Assigning responsibilities to specific IT and audit team members ensures accountability and timely resolution of findings.
4. Conduct Regular Audits
Routine audits help organizations stay ahead of potential risks. Scheduling audits quarterly, annually, or after major IT changes ensures continuous compliance and security improvements. Leveraging real-time monitoring tools enables proactive detection of vulnerabilities. Additionally, keeping the checklist updated with emerging threats, new technologies, and regulatory changes helps maintain IT resilience.
5. Document & Track Findings
Comprehensive documentation is key to tracking and resolving audit findings. All security gaps, vulnerabilities, and non-compliance issues should be documented with supporting evidence such as logs, screenshots, and access control reports. Using audit management tools like Netwrix, ServiceNow, or MetricStream streamlines tracking and remediation, ensuring no critical issue is overlooked.
6. Provide Actionable Remediation Steps
Addressing vulnerabilities effectively requires clear remediation steps. The checklist should outline specific corrective actions for each identified issue, assigning responsibilities to designated team members with clear deadlines. Ensuring compliance with security policies, data protection laws, and IT governance standards helps organizations maintain a robust security posture.
7. Verify & Follow Up on Improvements
After implementing corrective actions, it is essential to verify their effectiveness. Conducting follow-up audits ensures that fixes have been successfully applied. Testing security patches, policy updates, and system hardening measures validates improvements. Aligning risk mitigation strategies with long-term IT security goals fosters a proactive cybersecurity approach.
8. Maintain Compliance & Governance Standards
Compliance with regulatory frameworks is crucial for legal and operational security. The IT audit checklist should align with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOX, and other relevant standards. Keeping detailed audit logs facilitates legal and compliance reporting. Regular training for IT and security teams ensures they stay informed about evolving threats, policies, and best practices.
9. Automate Where Possible
Automation enhances the efficiency and accuracy of IT audits. Using audit software simplifies compliance tracking and security assessments. Implementing AI-driven monitoring systems helps detect anomalies in real time. Automating audit reporting reduces manual errors and streamlines the review process, ensuring greater reliability and efficiency.
10. Continuously Improve the Audit Process
The IT audit process should evolve alongside technological advancements and emerging risks. Regularly updating the checklist ensures it remains relevant to new threats, regulations, and infrastructure changes. Analyzing past audits helps identify patterns, trends, and recurring issues, allowing organizations to improve their security strategy. Encouraging a culture of proactive IT risk management strengthens long-term resilience and compliance.
Ensuring IT Compliance and Security Through Effective Audits
IT audits play a crucial role in identifying security vulnerabilities, ensuring regulatory compliance, and strengthening IT governance. A well-structured audit helps businesses proactively detect risks, protect sensitive data, and align IT operations with industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and ISO 27001. Without regular audits, organizations face increased exposure to cyber threats, financial penalties, and operational disruptions, making compliance and security essential for long-term success.
To maximize the effectiveness of IT audits, organizations should adopt a structured approach that includes risk assessments, control evaluations, compliance verification, and continuous monitoring. Leveraging audit management tools and automation can enhance accuracy and efficiency. For businesses lacking in-house expertise, seeking professional IT audit services ensures a thorough evaluation of security measures, regulatory adherence, and IT performance, helping them maintain a secure, compliant, and resilient IT environment.



