In today’s digital era, small businesses face an ever-growing risk of cyberattacks. From weak passwords and phishing scams to unpatched software and unsecured devices, cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities that can lead to devastating consequences like financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. With 60% of small businesses closing within six months of a cyberattack, robust cybersecurity measures are no longer optional—they’re essential. This guide provides 10 actionable cybersecurity tips, from using strong passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication to conducting regular backups and cybersecurity training, empowering small businesses to safeguard sensitive data, ensure compliance, and protect their operations against evolving threats.
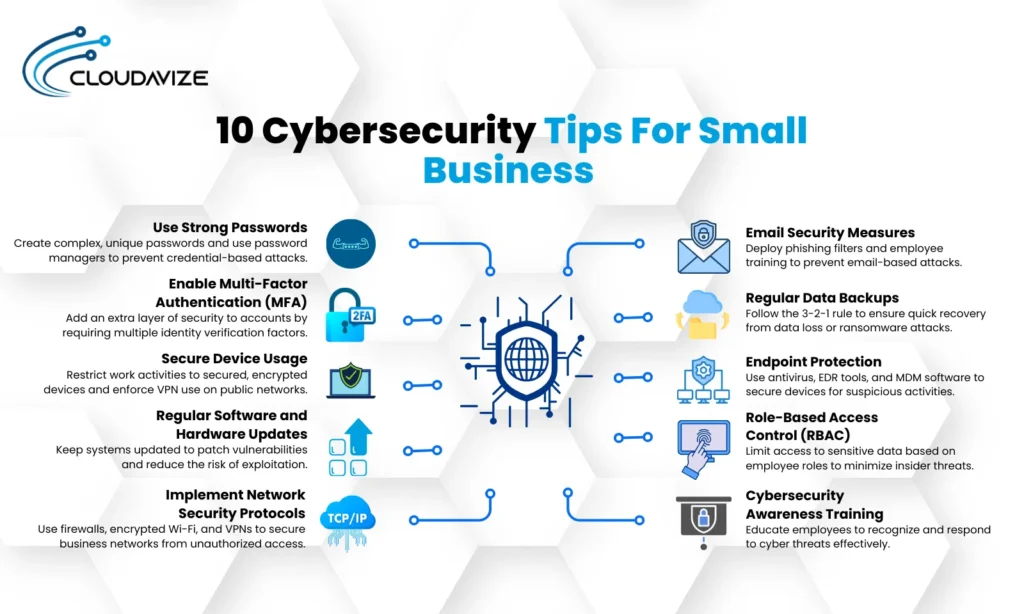
Table of Contents
1. Use Strong Passwords
Weak or reused passwords are a leading cause of cyberattacks, with 83% of breaches involving compromised credentials. Cybercriminals exploit simple passwords or predictable patterns, such as birthdays or common phrases like “123456.” For small businesses, the stakes are high—60% of companies shut down within six months of a cyberattack due to financial losses and reputational damage. Without strong passwords, even robust defenses like firewalls and antivirus software may fail to prevent unauthorized access, leading to potentially devastating consequences.
To mitigate these risks, businesses should implement strong password policies. Employees should create passwords with at least 12 characters, including a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols (e.g., T7m$qL2#vBn9). Using password managers like LastPass or 1Password can simplify managing unique passwords for each account. Additionally, enforce regular password updates every 90 days, especially for accounts with access to sensitive data. These practices form a vital first line of defense, protecting businesses from becoming easy targets for cybercriminals.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a vital security measure that requires users to verify their identity using two or more factors, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes. According to Microsoft, MFA blocks 99.9% of automated cyberattacks, making it a powerful tool for small businesses that are often targeted by credential-based attacks. Without MFA, stolen passwords can easily lead to data breaches, ransomware infections, or significant operational disruptions, leaving sensitive systems vulnerable to exploitation.
To effectively implement MFA, start by enabling it on critical systems like email accounts, financial tools, and cloud services. Prioritize secure methods such as app-based authenticators (e.g., Google Authenticator) or hardware tokens (e.g., YubiKey) over less secure SMS codes. Additionally, provide employees with training on recognizing phishing attempts and the importance of consistently using MFA. Tools like Duo or Okta simplify managing MFA across teams, ensuring a seamless and cost-effective deployment that strengthens data protection and enhances customer trust.
3. Secure Device Usage
Lost, stolen, or poorly managed devices present a significant cybersecurity risk for small businesses. Employees who use personal devices for work or access sensitive data over unsecured public Wi-Fi expose the organization to threats like malware infections, data breaches, and unauthorized access. A single compromised laptop or smartphone can leak sensitive customer data, financial records, or intellectual property—potentially leading to fines, legal consequences, and severe reputational damage. The growing prevalence of remote work exacerbates these vulnerabilities, as devices outside the office often lack adequate physical and digital protections.
To mitigate these risks, businesses should adopt strict device security policies. Restrict work activities to company-issued devices that are encrypted and configured with pre-set security controls. Enable full-disk encryption using tools like BitLocker for Windows or FileVault for macOS to secure stored data. Utilize mobile device management (MDM) software to remotely wipe data from lost or stolen devices and enforce security updates. Additionally, require remote employees to use VPNs on public Wi-Fi networks to ensure encrypted and secure internet connections. These measures safeguard critical data, enhance operational resilience, and reduce the risks associated with unmanaged device usage.
4. Regular Software and Hardware Updates
Outdated software and hardware are among the most exploited vulnerabilities in cyberattacks. According to the Ponemon Institute, 60% of data breaches result from unpatched systems, such as obsolete operating systems or unsupported applications. Hackers leverage these gaps to deploy ransomware, steal data, or take control of devices. Small businesses often delay updates due to concerns over cost or potential disruptions, but this hesitation can lead to catastrophic outcomes. For instance, the 2017 Equifax breach, caused by an unpatched web framework, exposed the sensitive data of over 140 million people, underscoring the risks of neglected updates.
To reduce these vulnerabilities, small businesses must adopt proactive patch management practices. Enable automatic updates for operating systems, software, and firmware, ensuring devices like routers and IoT systems remain secure. Replace unsupported hardware or software that no longer receives security patches, such as Windows 7 or outdated firewalls. Conduct quarterly audits to identify high-risk systems, prioritizing updates for critical tools like payment processors and databases. By maintaining updated systems, businesses can significantly minimize exposure to cyber threats and protect sensitive information.
5. Implement Network Security Protocols
Unsecured networks are a major vulnerability for small businesses, exposing them to risks such as unauthorized access, data interception, and malware infections. Public Wi-Fi, outdated routers, and unencrypted connections offer cybercriminals easy entry points to steal sensitive information or deploy ransomware. These vulnerabilities can compromise basic business operations, like payment processing or file sharing, damaging customer trust and violating compliance regulations such as GDPR.
To secure business networks, businesses should adopt a multi-layered approach. Deploy firewalls to monitor and block malicious traffic while securing Wi-Fi networks with WPA3 encryption and strong, unique passwords. Change default router credentials to prevent unauthorized access and segment networks to isolate guest or employee personal devices from critical systems like databases or payment processors. Regularly conduct network audits to identify vulnerabilities, such as outdated firmware or unpatched devices, and address them promptly. These protocols ensure a secure and reliable network infrastructure for small businesses.
6. Email Security Measures
Phishing attacks, responsible for over 90% of global data breaches, disproportionately affect small businesses. Cybercriminals impersonate trusted organizations like banks or vendors to trick employees into clicking malicious links, downloading infected files, or sharing sensitive login credentials. A single compromised email account can result in ransomware attacks, financial fraud, or unauthorized access to critical systems, potentially crippling operations and undermining customer trust.
To mitigate these risks, small businesses should prioritize email security. Deploy email filtering tools to block phishing emails, spam, and malware-laden attachments. Train employees to identify warning signs, such as urgent requests, typos, or mismatched sender addresses. Implement email authentication protocols like SPF (to verify sender IPs), DKIM (to ensure email integrity), and DMARC (to prevent spoofing). Additionally, encrypt sensitive communications to secure data during transmission. These measures not only safeguard business operations but also reinforce customer confidence in your organization’s cybersecurity practices.
7. Regular Data Backups
Ransomware attacks, hardware failures, and accidental deletions can severely disrupt small businesses, with downtime costing an average of $8,000 per hour (Datto). Cybercriminals often target backups to increase damage, leaving companies unable to recover critical data such as customer records, financial files, or inventory databases. Without reliable backups, businesses risk permanent data loss, missed compliance deadlines, and reputational harm—threats that can lead to business closure.
To safeguard against these risks, implement the 3-2-1 backup rule, a proven strategy for reliable data protection. Maintain three copies of your data: the original and two backups. Store these backups across two different media types, such as external drives and cloud storage, to reduce the risk of simultaneous failure. Additionally, ensure at least one copy is stored offsite using cloud services like Backblaze or AWS for geographic redundancy. These practices ensure that businesses can recover quickly from disruptions and maintain operational continuity.
8. Endpoint Protection
Endpoints, such as laptops, mobile devices, and IoT gadgets, are the most common targets for cyberattacks, with 94% of malware attacks directed at these devices (Webroot). Cybercriminals exploit outdated software, unsecured connections, and careless user behavior to deliver ransomware, spyware, and phishing payloads. A single compromised device can lead to data theft, network-wide breaches, or operational paralysis, with small businesses often facing significant recovery costs and productivity loss as a result.
To protect against these threats, small businesses should adopt a layered defense strategy. Install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software such as Bitdefender or Malwarebytes to block known threats in real-time. Utilize Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools like CrowdStrike or SentinelOne to monitor for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized file encryption, and automate threat containment. Enforce device management policies using Mobile Device Management (MDM) software to mandate encryption, apply patch updates, and restrict app installations to whitelisted programs. Additionally, continuously monitor endpoints to detect anomalies, including unusual login patterns or unexpected data transfers, ensuring timely responses to potential security breaches.
9. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Overly broad user permissions significantly increase the risk of insider threats, accidental data leaks, and privilege escalation. According to the 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report, 20% of breaches involve internal actors, either through negligence or malicious intent. Employees with unnecessary access to sensitive systems—like financial records or customer databases—can unintentionally expose data through phishing scams or mismanagement. For small businesses, these incidents can result in compliance violations, operational downtime, and expensive recovery processes.
Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) helps mitigate these risks by restricting access to only the tools necessary for an employee’s role. Define roles clearly by segmenting permissions based on job functions (e.g., accountants access payroll systems, while HR manages employee data). Follow the principle of least privilege (PoLP) by granting administrative rights to only a few trusted personnel. Conduct quarterly access audits to identify and remove outdated permissions, such as those belonging to former employees or employees with changed responsibilities. These practices ensure data security while reducing unnecessary exposure to insider risks.
10. Cybersecurity Awareness Training
Employees are often the weakest link in a business’s cybersecurity, with 45% of breaches attributed to human error, such as clicking on phishing links or mishandling sensitive data (CybSafe). Small businesses, which may lack sophisticated technical defenses, are particularly susceptible to social engineering tactics, ransomware, and accidental data leaks. A single mistake by an untrained employee can expose critical systems, leading to financial losses, compliance violations, and reputational harm, all of which can disproportionately impact smaller organizations.
To address these risks, businesses should invest in cybersecurity awareness training to empower employees as a proactive defense layer. Conduct quarterly training sessions that cover phishing recognition, identifying ransomware red flags, and secure password practices. Use interactive simulations and gamified learning tools like KnowBe4 or Proofpoint to reinforce knowledge and test real-world readiness. Foster a “no-blame” reporting culture to encourage employees to flag suspicious emails or incidents without fear of reprisal. Tailor specialized training for high-risk roles, such as finance teams for fraud prevention and IT administrators managing privileged access, to bolster security across the organization.
Why Cybersecurity matters for Small business?
Cybersecurity is essential for small businesses, which are prime targets for threats like ransomware, phishing, and data breaches. These attacks can lead to financial losses, compliance violations, and reputational harm. Protecting sensitive data and maintaining customer trust is critical for survival in today’s digital landscape. Providers like Cloudavize offer tailored cybersecurity solutions, including risk assessments, threat detection, and endpoint protection, helping small and medium-sized businesses reduce vulnerabilities and stay secure against evolving threats.



