Endpoint security safeguards devices like desktops, laptops, mobile devices, servers, and IoT devices from cyber threats. Key components include antivirus/anti-malware software, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Mobile Device Management (MDM), and technologies like real-time monitoring and threat detection. These measures are crucial, as 68% of firms have suffered one or more endpoint attacks compromising data or IT infrastructure, according to the Ponemon Institute.
Endpoint security solutions such as firewalls, Multi-factor Authentication (MFA), and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) enhance protection against unauthorized access and data breaches and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Organizations often rely on managed service providers (MSPs) to deploy and manage advanced endpoint security tools like Trend Micro XDR and Carbon Black, which employ AI for cross-layer detection and automated responses. According to Market.us, the global endpoint security market is projected to reach USD 36.5 billion by 2033, so investing in robust endpoint security is vital for mitigating risks and safeguarding digital assets.
Organizations benefit from endpoint cybersecurity Services through cost savings, faster incident response, and centralized management, while best practices like strong authentication, regular audits, and employee training address vulnerabilities such as phishing, malvertising, and IoT exploits. Endpoint security solutions, categorized as Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP), EDR, Extended Detection and Response (XDR), and Managed Detection and Response (MDR), cater to diverse organizational needs. Prominent examples, including Microsoft Defender and CrowdStrike Falcon, provide scalability, advanced analytics, and real-time threat intelligence for comprehensive protection.
Table of Contents
What Is Endpoint Security/Endpoint Protection?
Endpoint security, or endpoint protection, refers to the strategies and technologies that safeguard endpoint devices such as desktops, laptops, mobile devices, servers, and IoT devices against cyber threats. These devices, or endpoints, serve as entry points for cybercriminals, making their security crucial for overall network integrity. Securing each endpoint is essential to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and other malicious activities that could compromise the entire network.
Endpoints are pivotal in network security, acting as potential gateways for cyber threats. Key mechanisms of endpoint security include real-time monitoring, threat detection, and response capabilities to identify and mitigate risks promptly. Comprehensive endpoint security solutions employ multiple layers of defense, such as antivirus/anti-malware software, firewalls, and advanced tools like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) systems and Mobile Device Management (MDM) platforms.
A robust endpoint security solution comprises various components designed for holistic protection. Examples include Antivirus/Anti-malware software for detecting and removing malicious software, EDR systems for continuous threat monitoring and response, and MDM platforms for enforcing security policies on mobile devices. Other essential components are Network Access Control (NAC) solutions, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools, email security gateways, patch management systems, Multi-factor Authentication (MFA), and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), collectively ensuring comprehensive protection against endpoint vulnerabilities.
Why Is Endpoint Security Important?
Endpoint security is a cornerstone of cybersecurity that is critical for preventing data breaches and protecting sensitive data on devices from unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Specific features such as encryption, access controls, and advanced threat detection are integral to preventing breaches. For instance, data encryption ensures that sensitive information like personal details, financial records, and intellectual property remains secure during transmission. Access controls limit who can view or modify data, reducing the risk of internal threats.
Endpoint security is essential for compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), helping businesses avoid fines and legal penalties and maintain customer trust. Protecting sensitive data is not only about regulatory compliance but also about ensuring business continuity. Cyberattacks can disrupt operations, leading to significant financial losses and damage to reputation. According to a report by Morphisec, 81% of firms experienced attacks involving some type of malware, highlighting the pervasive risk. By implementing endpoint security measures such as regular security audits and secure access controls, businesses can prevent disruptions, retain customer trust, and safeguard their competitive advantage in the market.
Here are some real-world examples of data breaches and how effective endpoint security could have prevented them
- Equifax (2017):
A critical vulnerability in the Apache Struts web application framework was exploited, exposing the personal data of 145.5 million people.
Prevention: Timely patch management and vulnerability scanning could have identified and addressed this weakness before it was exploited.
- Target (2013):
Attackers gained access through a third-party HVAC vendor’s credentials, eventually compromising point-of-sale systems and stealing the credit card data of 40 million customers.
Prevention: Stronger access controls, network segmentation, and endpoint monitoring could have detected and prevented the lateral movement of the attackers.
- SolarWinds (2020):
Attackers inserted trojanized (malicious) code into SolarWinds’ Orion software updates. As a result, nearly 18,000 customers received a compromised software update.
Prevention: Advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems could have identified the abnormal behavior of the compromised software.
- Colonial Pipeline (2021):
A ransomware attack via a compromised VPN account led to a significant fuel pipeline shutdown. The attackers accessed nearly 100 GB of data. A ransom of 75 Bitcoins (USD4.4 million) was paid for the decryption key.
Prevention: Multi-factor authentication and more robust endpoint security measures could have prevented the initial unauthorized access.
- Marriott International (2018):
A breach of the Starwood guest reservation database exposed the personal information of up to 500 million guests.
Prevention: Data encryption, access controls, and continuous database activity monitoring could have mitigated this breach’s impact.
Key Benefits of Endpoint Security
Key benefits of endpoint security range from comprehensive threat protection, cost savings, and improved compliance to enhanced productivity and faster incident response. Endpoint security is essential to ensure robust protection against diverse cyber threats, support the secure operation of digital environments, improve overall security posture, mitigate risks, and support the seamless functionality of organizations.
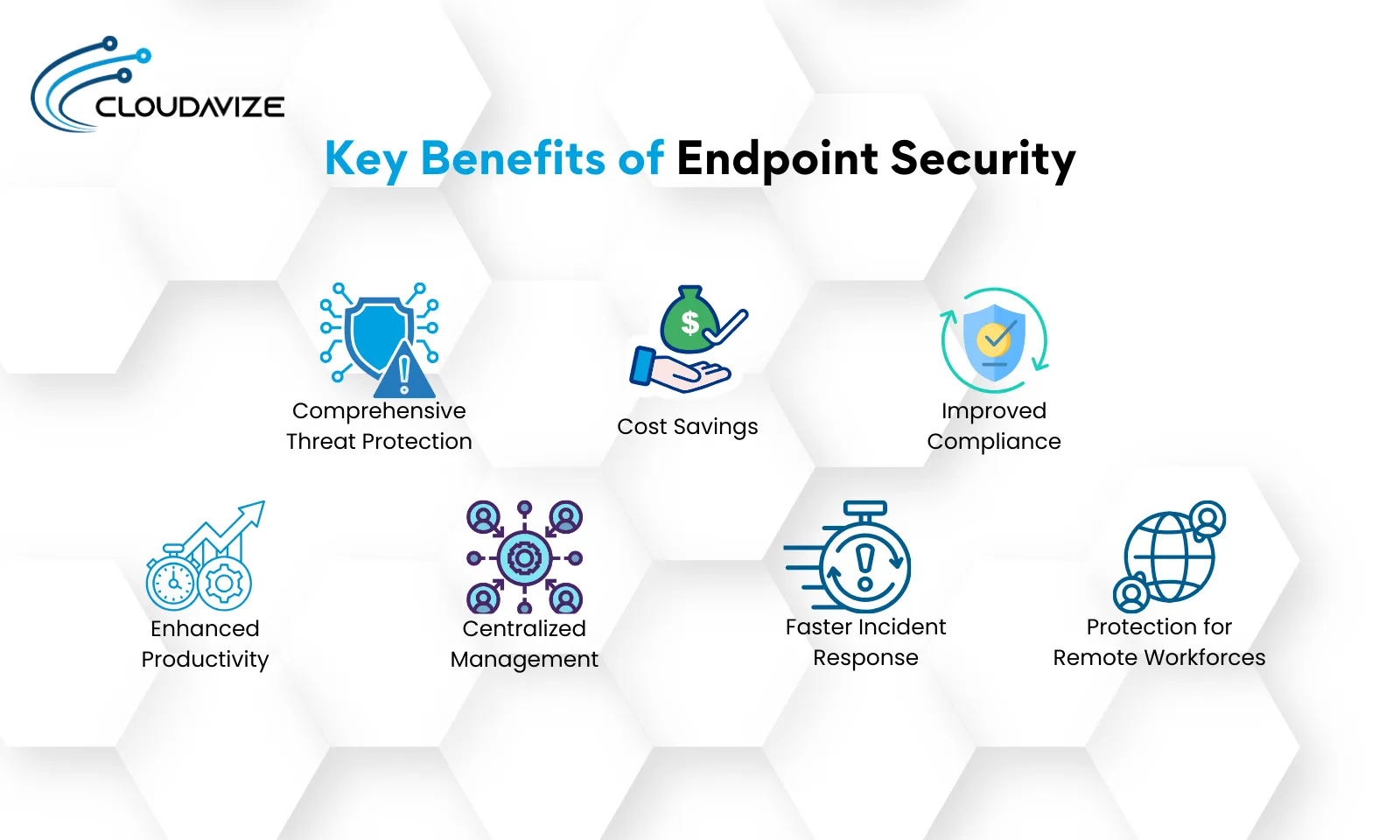
Comprehensive Threat Protection
With endpoint security, organizations are safeguarded against various cyber threats, including malware, ransomware, phishing, and zero-day exploits. Protecting sensitive data and maintaining privacy is crucial to reducing the risk of data breaches. Endpoint security protects sensitive data and maintains business operations and customer trust by employing encryption, access controls, and advanced threat detection.
Cost Savings
Investing in endpoint security contributes to significant cost savings by preventing data breaches, reducing downtime, and minimizing the financial impact of cyber incidents. Robust endpoint security solutions provide long-term economic benefits, shielding businesses from the costly consequences of cyberattacks.
Improved Compliance
Endpoint security helps organizations comply with industry regulations and standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. Maintaining compliance is essential for avoiding fines and legal penalties, ensuring business credibility, and making endpoint security an integral part of regulatory adherence.
Enhanced Productivity
Minimizing disruptions from security incidents is vital in enhancing productivity. Endpoint security ensures secure access to resources, supports remote work, and maintains a seamless workflow. By reducing the frequency and impact of cyber threats, endpoint security allows employees to focus on tasks without interruption, boosting overall efficiency.
Centralized Management
Centralized management provided by endpoint security platforms enables IT administrators to monitor, manage, and secure all endpoints from a single console. This approach streamlines operations, reduces administrative overhead, and improves oversight of the organization’s security posture. The ability to manage multiple security functions from one place results in significant efficiencies and enhanced control.
Faster Incident Response
Endpoint security’s significant advantage is its ability to detect and respond to security incidents quickly. Technologies like real-time monitoring, automated threat response, and behavioral analysis tools allow for rapid incident detection and mitigation. This swift response minimizes potential damage, reduces recovery time, and ensures business operations can continue with minimal disruption.
Protection for Remote Workforces
In today’s remote work environment, protecting remote devices and ensuring safe connections to corporate networks is more critical than ever. Endpoint security addresses these unique challenges by securing remote endpoints and facilitating safe, reliable access to corporate resources. This protection is essential for maintaining the security and productivity of remote workers, who are often targeted by cybercriminals due to less secure home networks.
Types of Endpoint Security Solutions
Types of endpoint security solutions are Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP), Endpoint Detection and Remediation (EDR), Extended Detection and Response (XDR), and Managed Detection and Response (MDR). They protect technology infrastructure against diverse cyber threats, safeguard sensitive data, and maintain the overall security of an organization’s network. Understanding these different types can help businesses implement the most effective security measures.
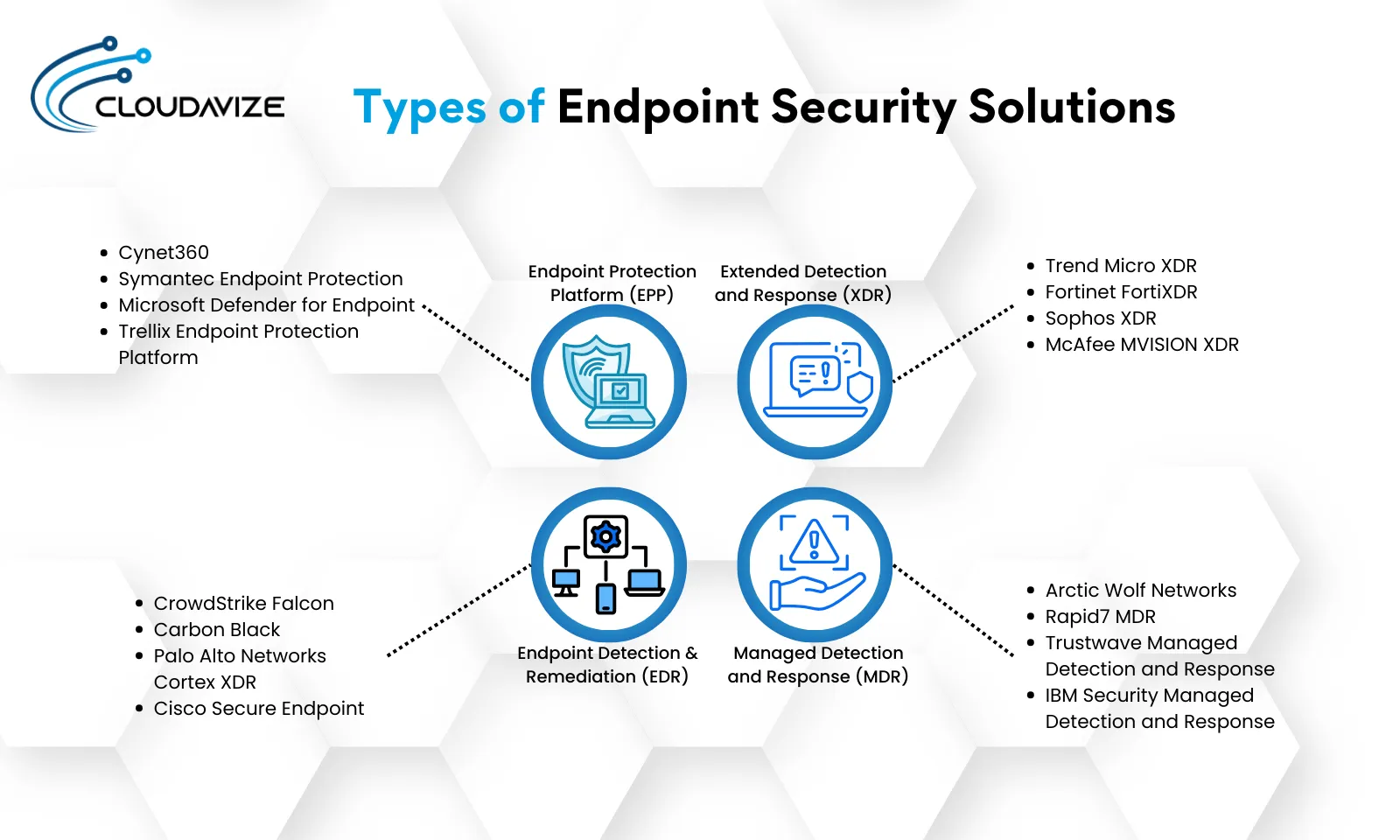
Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP)
Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP) are designed to prevent endpoint threats by providing comprehensive protection. EPPs typically include antivirus, anti-malware, and firewall capabilities.
Some of the popular EPP solutions are:
- Cynet360: Cynet360 offers integrated threat detection and response, automated investigation and remediation, behavioral analysis, and fileless attack protection. Benefits include comprehensive protection across all endpoints, reduced incident response time, and enhanced detection of sophisticated threats. It is available in Elite and All-in-One packages. You can request a quote to know the pricing details.
- Symantec Endpoint Protection: Symantec Endpoint Protection features advanced machine learning, exploit prevention, network firewall, device control, and intrusion prevention. It offers robust malware protection, prevention of zero-day attacks, and secure network communications. It will cost you $39 for a one-year subscription license with essential support.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint provides real-time threat detection, automated investigation and remediation, EDR, and threat and vulnerability management, improving threat visibility and quick incident resolution. It is available as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint P1 and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint P2, which are included in Microsoft 365 E3 and E5, respectively.
- Trellix Endpoint Protection Platform: Trellix Endpoint Protection Platform offers a comprehensive solution for safeguarding organizational endpoints against evolving cyber threats. Leveraging AI-driven threat intelligence, the platform provides real-time protection by accurately identifying and neutralizing potential risks. Its dynamic application containment feature isolates suspicious activities, preventing the spread of threats across the network. Trellix Endpoint Security (TRXE1) is available at an annual fee of $136.16 per user.
Endpoint Detection and Remediation (EDR)
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) focuses on detecting and responding to advanced threats through continuous monitoring and analysis. EDR solutions are essential for identifying and mitigating sophisticated attacks.
- CrowdStrike Falcon: CrowdStrike Falcon is a cloud-native platform offering real-time threat detection, AI-driven analytics, endpoint protection and response, and threat intelligence integration, providing high scalability and immediate threat visibility. Falcon Pro for enterprise costs $99.99/device per year while costing $8.33/device per month. Other available packages are Falcon Enterprise ($184.99/ device per year), and Falcon Elite.
- Carbon Black: Carbon Black features behavioral analytics, continuous recording, attack chain visualization, real-time response, and threat hunting, enabling proactive threat detection and detailed attack insights. You can buy Endpoint Standard for $40 per endpoint, Endpoint Advanced for $60 per endpoint, and Endpoint Enterprise for $90 per endpoint.
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR: Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR offers unified data collection, AI-driven detection, automated response, and cross-data correlation for seamless security-level integration. You get two options: Coretx XDR Prevent ($16,000/year for 200 seats) and Cortex XDR Pro ($14,000/year for 200 seats).
- Cisco Secure Endpoint (formerly AMP for Endpoints): Cisco Secure Endpoint, previously known as AMP for Endpoints, is a comprehensive endpoint security solution that offers advanced protection against cyber threats. It provides advanced malware protection, continuous endpoint monitoring, retrospective security, and cloud-delivered threat intelligence. Three available plans include Secure Endpoint Essentials, Secure Endpoint Advantage, and Secure Endpoint Premier.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) extends threat detection and response capabilities across multiple security layers, including network, server, and endpoint.
- Trend Micro XDR: Trend Micro XDR is an advanced security solution that leverages cross-layer detection, AI-driven analytics, and automated response capabilities to provide comprehensive protection against complex cyber threats. Correlating data from multiple security layers, including email, endpoints, servers, cloud workloads, and networks, enhances detection accuracy and enables proactive threat intelligence. To acquire a one-year subscription, you need to pay $69.99 for a user.
- Fortinet FortiXDR: Fortinet FortiXDR is an advanced endpoint security solution that leverages AI-driven detection and automated investigation to provide comprehensive protection across various layers of an organization’s IT infrastructure. By automating the investigation process, FortiXDR significantly reduces response times, allowing security teams to focus on critical tasks rather than manual threat hunting.
- Sophos XDR: Sophos XDR (Extended Detection and Response) is a comprehensive security solution that combines endpoint, network, and cloud data in a unified data lake. It leverages AI-enhanced detection and advanced threat-hunting capabilities to identify and neutralize sophisticated cyber threats. You can request a quote to get the pricing description.
- McAfee MVISION XDR: McAfee MVISION XDR is a cloud-native extended detection and response solution that offers comprehensive visibility across an organization’s entire ecosystem. Its integrated threat intelligence provides improved context for faster, more accurate threat detection and response, enabling organizations to efficiently protect against advanced threats in an increasingly complex digital landscape. Its subscription costs an annual fee of $168.99 for a subscription license and business software support.
Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) services provide managed security solutions that use third-party providers to detect and respond to threats.
- Arctic Wolf Networks: Arctic Wolf Networks offers comprehensive endpoint security with 24/7 monitoring, personalized threat detection, and dedicated SOC support. This solution provides continuous protection and tailored security insights backed by expert threat response to safeguard organizations against evolving cyber threats. You can get insights into its pricing model by requesting a quote.
- Rapid7 MDR: Rapid7 MDR offers real-time threat detection, incident response, and threat intelligence integration, enabling organizations to promptly identify and address security threats. This comprehensive solution provides immediate threat identification, efficient incident handling, and enriched context through integrated threat intelligence, enhancing overall security posture and reducing response times. Various packages like MTC Essential, MTC Advanced, and MTC Ultimate are available.
- Trustwave Managed Detection and Response: Trustwave Managed Detection and Response offers advanced threat detection, global SOC support, and proactive threat hunting to enhance an organization’s cybersecurity posture. This comprehensive solution provides enhanced detection capabilities, round-the-clock support, and proactive identification of emerging threats, enabling businesses to avoid potential security breaches. You can fill out the form to request a pricing quote.
- IBM Security Managed Detection and Response: IBM Security Managed Detection and Response offers AI-driven threat detection, comprehensive incident response, and integrated threat intelligence. This solution provides accurate threat detection through incident handling and enables informed decision-making through advanced threat intelligence, enhancing an organization’s security posture. EDR SaaS costs $3,888/year, while EDR Software costs $3,633/year.
Understanding Attack Vectors in Endpoint Security
Understanding attack vectors in endpoint security includes phishing emails, malvertising, physical devices, password vulnerabilities, and the Internet of Things. Attack vectors are the pathways or methods cybercriminals use to infiltrate endpoint devices and networks, exploiting vulnerabilities to compromise data and system integrity.

Phishing Emails
Phishing is a cyberattack method that involves tricking recipients into revealing sensitive information or installing malware through deceptive emails. These attacks often use deceptive links, fake websites, and social engineering tactics. According to Ponemon Institute research, 68% of firms had suffered one or more endpoint assaults that successfully compromised data and/or IT infrastructure, with attacks against endpoints being among the most common. Email security measures like spam filters, employee training, and multi-factor authentication are essential to combat phishing attacks.
Digital Advertising (Malvertising)
Malvertising, or malicious advertising, operates within digital advertising to spread malware. It involves methods like redirecting users to malicious websites and automatic malware downloads. According to Webroot research, 83% of malware threats are kept in one of four locations: %tmp%, %appdata%, %cache%, and %desktop%. Prevention strategies include using ad-blockers, updating software, and employing web security solutions to block malicious ads and ensure a safe browsing experience.
Physical Devices (USBs and Removable Media)
Using physical devices like USBs and removable media in endpoint security presents significant risks. Examples of security threats include malware-laden USBs and unauthorized data copying. More than 70% of data loss incidents originate on employee endpoints, highlighting the critical nature of this issue. Organizations should implement strict security policies to mitigate these risks, use endpoint protection software, and educate employees about the dangers of using unknown devices.
Password Vulnerabilities
Password vulnerabilities pose a substantial threat to endpoint security. These vulnerabilities can be exploited through brute force attacks, phishing, and credential stuffing. Best practices to enhance password security include using strong, unique passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Due to their widespread use and varying levels of security, IoT devices present unique security challenges. Security risks include unauthorized access, data breaches, and botnet attacks. Effective strategies to secure IoT devices involve using strong passwords, regularly updating firmware, and employing network segmentation to isolate them from critical systems.
Best Practices For Securing Endpoints
Best practices for securing endpoints range from using strong authentication methods, implementing EDR solutions, and using antivirus software to implementing data encryption, access control, and regular security awareness training. Securing endpoints is essential in protecting organizational data and maintaining the integrity of network systems. Implementing robust security measures can prevent unauthorized access and safeguard against cyber threats.
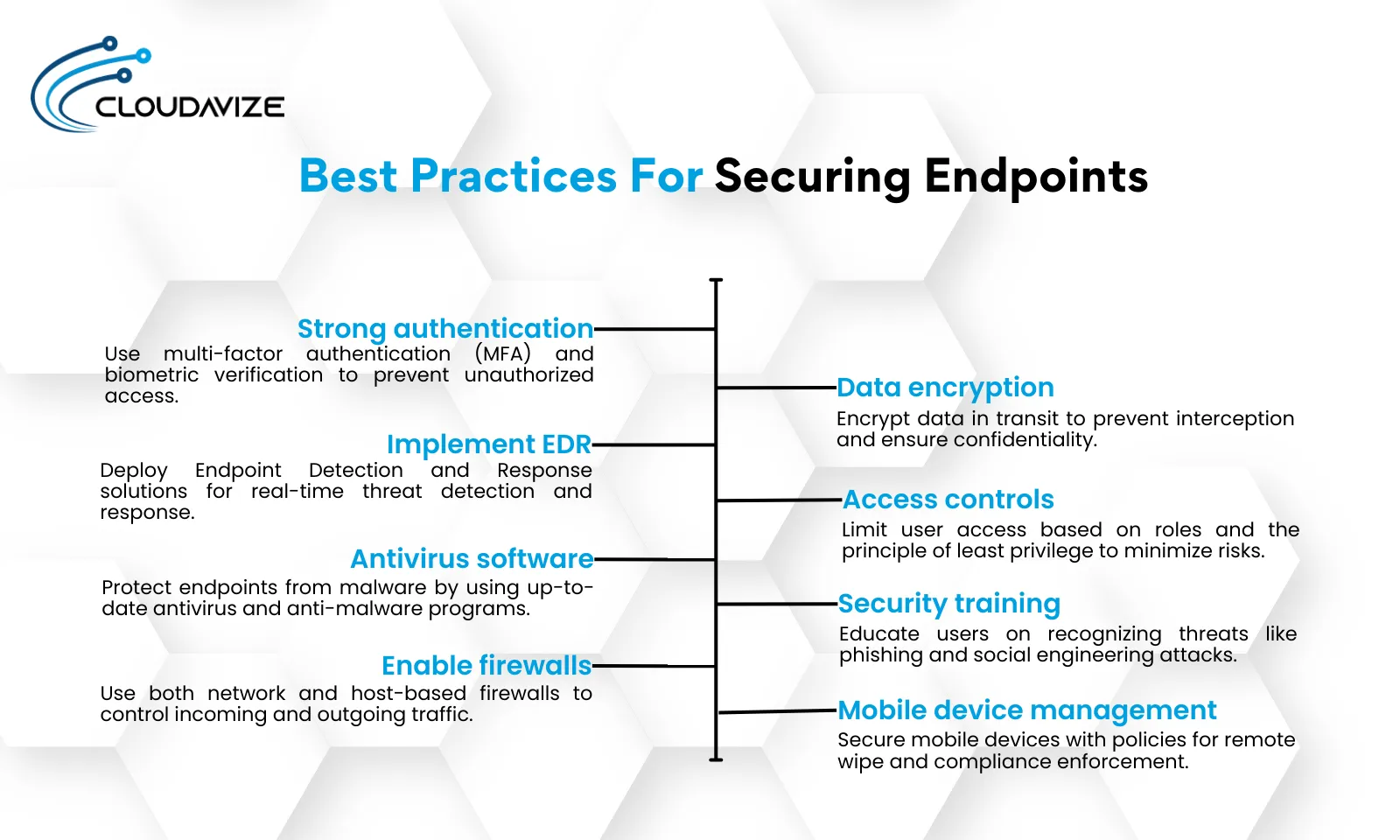
Use Strong Authentication Methods
Strong authentication methods are crucial for preventing unauthorized access and reducing the risk of credential theft. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric verification significantly enhance security by requiring multiple verification methods before granting access. Implementing these methods ensures that even if one credential is compromised, additional layers of security protect sensitive information.
Implement EDR Solutions
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions are vital for monitoring endpoint activity to detect, investigate, and respond to suspicious behavior. EDR solutions provide real-time visibility and advanced threat detection capabilities. They continuously analyze endpoint data, allowing security teams to identify and mitigate threats quickly, reducing potential damage and maintaining endpoint integrity.
Use Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Antivirus and anti-malware software are necessary for protecting endpoints from malicious software. These programs detect and remove various types of malware, including viruses, ransomware, and spyware. Updating this software is crucial for combating new threats and ensuring endpoints are protected against the latest cyber risks.
Enable Firewalls
Firewalls are critical in securing endpoints by controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Network-based firewalls protect the entire network, while host-based firewalls provide an additional layer of defense at the endpoint level. Using both types of firewalls creates multiple layers of protection, enhancing overall security.
Use Data Encryption for Transit
Data encryption, particularly for data in transit, is essential for preventing data interception and ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. Encryption protocols like SSL/TLS and VPNs protect data as it moves across networks, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties. This measure is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information during transmission.
Implement Access Controls and Least Privilege Practices
Access controls and the principle of least privilege are fundamental for limiting user access to necessary resources only. This practice reduces the risk of internal threats and data breaches. Role-based access control (RBAC) and identity management systems help manage and enforce these policies, ensuring users have appropriate access levels.
Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training for Users
Regular security awareness training for users is vital in helping employees recognize and respond to security threats. Training topics should include phishing attempts, social engineering attacks, and other common threats. Engaging and informative sessions ensure that users stay vigilant and informed about the latest security practices.
Use Mobile Device Management (MDM) for Portable Devices
Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions are critical for securing portable devices such as smartphones and tablets. MDM helps enforce security policies, remotely wipe data if devices are lost or stolen, and ensure compliance with security standards. Securing mobile devices is increasingly important due to their widespread use and vulnerability to cyber threats.
Utilize Cybersecurity Management Services for Robust Protection
Cybersecurity management services deliver a comprehensive endpoint protection strategy by integrating advanced monitoring, proactive threat detection, and effective response solutions. These services are designed to adapt and evolve, ensuring businesses remain resilient against emerging cyber threats.Cloudavize specializes in creating tailored cybersecurity solutions to meet diverse organizational needs. Their offerings include endpoint protection, access control implementation, and state-of-the-art threat detection tools, ensuring robust security for your digital assets.
What Should You Look for in an Endpoint Protection Platform?
In an endpoint protection platform, you should look for various factors, including comprehensive protection, real-time threat detection and response, a user-friendly interface, scalability, and compatibility. Selecting the right Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP) is critical for enhancing overall endpoint security and meeting an organization’s specific needs.
- Comprehensive Protection: Comprehensive protection is crucial for endpoint security as it covers many threats, including malware, ransomware, phishing, and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). Multi-layered security features improve threat detection and reduce the risk of breaches. An EPP with comprehensive protection ensures that endpoints are safeguarded against diverse cyber threats, maintaining the integrity and security of organizational data.
- Real-Time Threat Detection and Response: Real-time threat detection and response are vital for effective endpoint security. Machine learning and behavioral analysis enable quick identification and mitigation of threats. Real-time capabilities offer significant benefits, including faster threat identification, quicker mitigation, and reduced impact of security incidents, ensuring continuous protection.
- User-Friendly Interface and Centralized Management: A user-friendly interface is essential for effective endpoint management. Centralized management streamlines operations and improves oversight by allowing administrators to monitor and secure all endpoints from a single console. This reduces administrative overhead and enhances overall efficiency, making endpoint management more straightforward and effective.
- Scalability and Compatibility: Scalability and compatibility are crucial for growing organizations. An EPP should support diverse endpoints, integrate seamlessly with existing systems, and handle increased data volumes. Cloud-based platforms and solutions with broad device support exemplify scalability and compatibility, ensuring that the EPP can grow with the organization’s needs.
- Performance Impact: Evaluating the performance impact of an EPP on endpoint devices is essential to balance security with performance. Criteria include resource usage, system slowdown, and user experience. Optimizing settings, using lightweight agents, and conducting regular performance assessments help minimize the performance impact while maintaining robust security.
- Reporting and Analytics: Comprehensive reporting and analytics are essential for maintaining a strong security posture. Features to look for include real-time dashboards, trend analysis, and detailed incident reports. EPP solutions excelling in reporting and analytics provide detailed insights and actionable intelligence, helping organizations respond effectively to security incidents.
- Cost and Licensing: Understanding an EPP’s cost and licensing structure is crucial for budgeting and financial planning. Factors to consider include initial costs, ongoing subscription fees, scalability costs, and potential hidden charges. Cost-effective EPP solutions with transparent licensing models ensure organizations can plan their security investments without unexpected expenses.
- Support and Maintenance: Support and maintenance are critical aspects of an EPP. Look for solutions offering 24/7 availability, knowledgeable support staff, and comprehensive service agreements. EPP solutions, known for exceptional support and maintenance services, ensure that organizations have the necessary assistance to address any security issues promptly.
- Behavioral Analysis and Threat Intelligence Integration: Behavioral analysis and threat intelligence are vital for modern endpoint protection. Mechanisms of behavioral analysis and integration with threat intelligence provide proactive security measures. EPP solutions excelling in these areas enhance threat detection and response, ensuring comprehensive protection against sophisticated threats.
- Ease of Deployment and Employee Training: Ease of deployment and thorough employee training are critical for successfully adopting an EPP. Considerations include intuitive setup processes, minimal disruption during deployment, and effective training modules. EPP solutions that are easy to deploy and offer robust training support ensure that employees are well-prepared to use the platform effectively.
FAQs
Are Endpoint Security and Antivirus the same?
No, endpoint security and antivirus are not the same. Antivirus software is a component of endpoint security, which offers a broader range of protective measures, including threat detection, firewall protection, and real-time monitoring, to safeguard endpoint devices comprehensively.
Difference Between Endpoint Security Vs. Network Security ?
Endpoint security protects individual devices, such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices, from cyber threats, whereas network security secures the entire network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and servers, to prevent unauthorized access and attacks.
Is VPN an Endpoint Security?
No, a VPN is not an endpoint security solution. It is a tool that provides secure, encrypted connections for remote access but does not encompass the full range of protective measures offered by endpoint security solutions, such as malware detection, threat response, and data encryption for endpoints.



