Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks, using technologies such as firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication to ensure the credibility and availability of digital assets and safeguard sensitive information. It is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining business operations, as cyber threats like social engineering, malware, DDoS attacks, and AI-powered attacks continue to evolve. Effective cybersecurity strategies include regular vulnerability assessments, employee training, and the implementation of robust security policies. The field encompasses various types of security, including network, data, cloud, IoT, and zero trust models, each addressing specific protection needs. Cybersecurity professionals require a range of skills, from network security and incident response to understanding regulatory frameworks, and can pursue diverse career paths, from security analysts to CISOs. Emerging trends, such as the use of AI in threat detection and the challenges posed by IoT devices, underscore the need for continuous adaptation and investment in cybersecurity measures.
Table of Contents
Importance of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is essential for protecting data, business, and privacy in an increasingly digital world. As businesses and individuals become more reliant on technology, the risks of cyber threats like data breaches, intellectual property theft, and reputational damage increase. Without a solid cybersecurity strategy, organizations will suffer financial and operational losses, so cybersecurity is essential for individuals and businesses.
To combat these threats, firewalls and intrusion detection systems protect your digital assets by blocking access and responding quickly to threats. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are essential to finding and fixing security weaknesses and encryption technologies that secure sensitive transactions. Training your employees on security practices and trends will strengthen your organization’s defenses. Regular system updates and multi-factor authentication will protect your digital environment, regulatory compliance, and customer and stakeholder trust.
Common Types of Cybersecurity Threats To Be Aware of in 2025
Common cybersecurity threats you must be aware of in 2025 include social engineering, malware, DDoS, MITM, AI-powered attacks, and DNS tunneling. To tackle the increasing number and methods of threats, it is essential to opt for effective cybersecurity strategies tailored to strengthen security, protect digital assets, and maintain a smooth business operation.
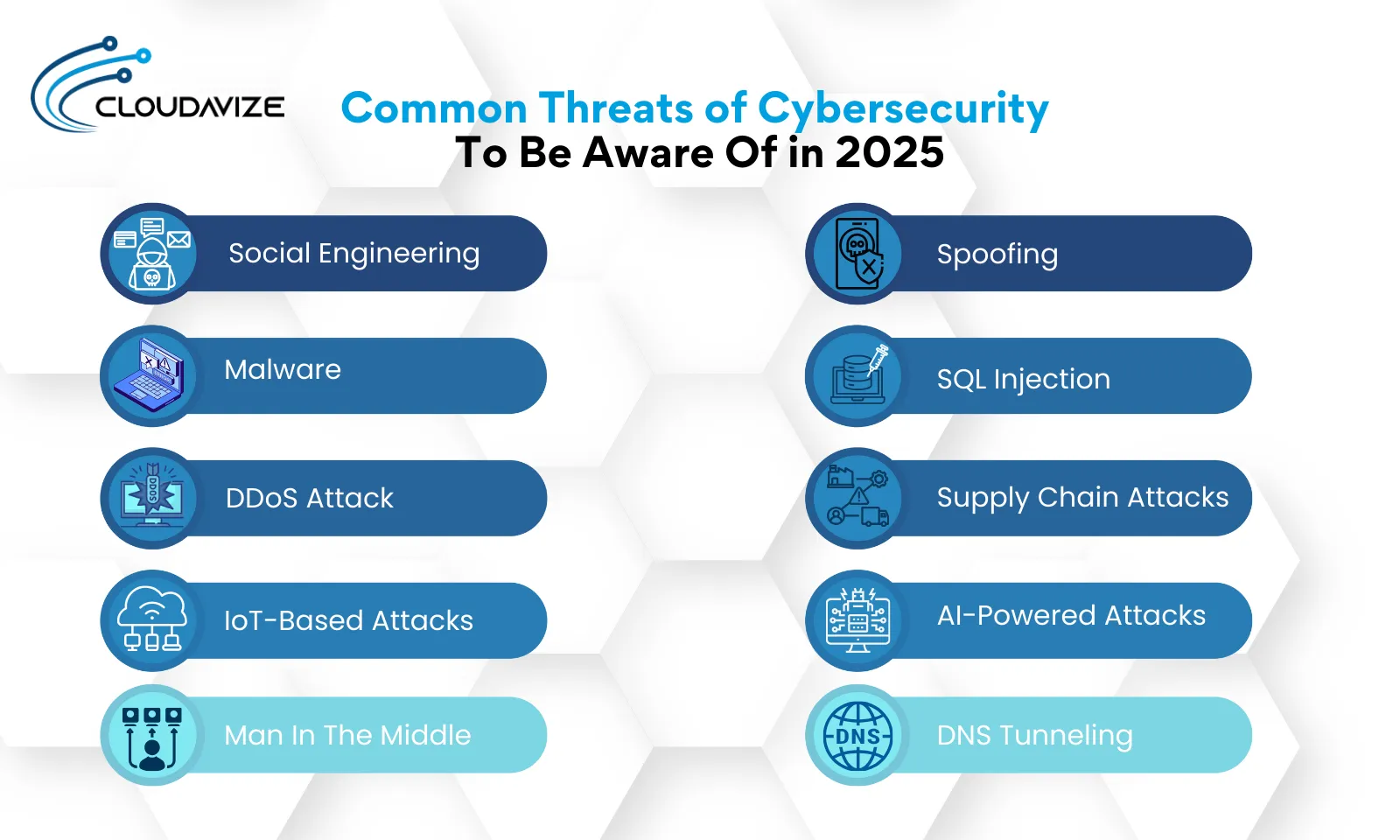
- Social Engineering: Social engineering Involves manipulating or deceiving an individual to access confidential information or compromise security. Common methods include phishing and identity-based attacks. Phishing uses deceptive emails/messages to obtain personal information, while Identity-based attacks exploit personal information for unauthorized access to systems and data.
- Malware: Malware is malicious software cybercriminals use to damage, steal, and destroy information or take control of a computer system. Common examples are:
- Ransomware: Used to demand ransom to release encrypted data.
- Viruses and worms: Spreads throughout the system, corrupting and damaging the system.
- Spyware: Collects user data without consent.
- Adware: Displays unwanted ads, leading to privacy breaches and slowing the system.
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS) Attacks: DDoS attacks try to disrupt a target network or service with overwhelming internet traffic, rendering it inaccessible. These attacks cripple online services and cause significant disruptions.
- IoT Based Attacks: IoT-based attacks target Internet of Things (IoT) devices, exploiting their weak points. IoT attacks range from unauthorized access to botnet attacks, which compromise the entire network due to the interconnectedness of devices.
- Man In The Middle (MITM): MITM occurs when attackers intercept and change the communication between two entities. Common MITM scenarios include eavesdropping on public Wi-Fi and session hijacking, which can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information and systems.
- Spoofing: In Spoofing, attackers disguise themselves as legitimate entities to deceive their targets and obtain confidential information. IP Spoofing uses forged IP addresses to impersonate devices, while Email Spoofing uses email addresses with forged sender addresses.
- SQL Injection: SQL injection Uses malicious SQL code to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications. It leads to unauthorized access to the company’s database, which usually results in data manipulation. It critically hampers the organization’s integrity and reputation.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Supply chain attacks target an organization’s supply chain to compromise its security. Common tactics include compromising third-party vendors and inserting malicious code, which can then infiltrate the primary organization’s systems and data.
- AI-Powered Attacks: AI-powered attacks leverage AI to enhance the effectiveness and scalability of attacks. Common examples are automated phishing and deepfake technology aimed to produce fraudulent content to deceive victims and bypass traditional measures.
- DNS Tunneling: DNS tunneling exfiltrate data or communicate with malware through DNS queries. This method encapsulates data from other protocols within DNS queries and responses, allowing for covert communication and data exfiltration through the DNS protocol, often bypassing standard security measures.
Top 10 Best Practices To Protect Yourself Against CyberSecurity Threats & Attacks
To remain safe and secure against cybersecurity threats and attacks, it is essential to adopt preventive measures and pursue best industry practices such as:

- Regular Vulnerability Scanning: Helps proactively detect and mitigate vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Scheduling regular scans can help detect the latest threats and deal with them accordingly.
- Penetration Testing: Uncovers security gaps while strengthening defenses. It is necessary to conduct periodic tests and have qualified security experts perform comprehensive assessments.
- Awareness & Training: Train employees and conduct workshops to inform them of the latest trends, which can help mitigate breaches.
- Implement Cybersecurity Policy (BYOD): Protect data on personal devices by implementing robust cybersecurity policies. Use encryption and strong authentication, and regularly update the devices to address emerging threats.
- Install Firewall: Do this at network entry points, use advanced features like intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and regularly update firmware to prevent unauthorized access and network integrity.
- Update your software and operating systems regularly: Use automatic updates for software and operating systems. It safeguards systems from known exploits while maintaining system security.
- Implement Endpoint Protection (Remote Workers): Deploy comprehensive endpoint protection software, enforce strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regularly update the software to guard against new threats.
- Limited Access To System: Use role-based access control (RBAC) to manage user permissions and regularly review and adjust access rights to align with job roles.
- Enhance Wifi Security: Enhancing WiFi security prevents attacks such as eavesdropping and data theft. Use strong encryption protocols like WPA3, change default router settings, and regularly update firmware to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Strong Passwords and Multiple-factor Authentication (MFA): Use strong passwords comprising alphanumeric and special characters and implement MFA for an extra layer of security. Encourage a culture of regular password changes to prevent security breaches.
While these security measures are critical, managing them effectively can be overwhelming for businesses. This is where a Managed Service Provider (MSP) steps in, offering Managed Cybersecurity Services to handle your security needs so you can focus on growing your business without worrying about cyber threats.
Leveraging Managed Cybersecurity Services
An MSP (Managed Service Provider) provides Managed Cybersecurity Services that take the burden of security off your shoulders. By partnering with an MSP, businesses can focus on their core operations while experts manage their cybersecurity infrastructure. MSPs offer end-to-end solutions, including vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, employee training, and 24/7 monitoring, ensuring your business remains protected against evolving threats. With an Managed Service Provider, you gain peace of mind knowing that your cybersecurity is in the hands of professionals, allowing you to concentrate on what you do best—running your business.
How Much Do Managed Cybersecurity Services Cost?
Managed cybersecurity services cost between $4 and $9 per device per month. If you get the per-user pricing, the rate falls between $75 and $100 per user per month. Various factors, such as the complexity of the IT environment, organization size, service level requirements, and tailored cybersecurity needs, influence the cost of Managed Cybersecurity Services. Knowing these costs helps in making informed decisions while choosing specific cybersecurity options.
- Monthly Rates: They are scaled at $4.00 per device per month. A Premier plan is available at $6.25 per device per month, while an Enterprise plan comes at $9.00 per device per month. The price increases for larger organizations or more complex needs.
- Per User Pricing: Costs range between $75 and $100 per user per month. This model suits businesses with fixed employees and allows predictable budgeting.
- Per Device Pricing: This model is available at $4.00 per device per month for standard management and goes up to $9.00 per device per month for the most comprehensive plan.
- Tiered and Flat-Fee Models: Packages range from $3,000 to $6,000 per month. The tiered model provides basic to premium services, while the Flat-fee model offers comprehensive support for a fixed monthly cost.
- Hourly Rates: This model suits businesses with irregular IT support needs or project-based work. It costs between $150 and $199 per hour.
What are the Types of Cybersecurity
There are mainly 7 types of cybersecurity, each addressing specific areas of protection to safeguard against evolving cyber threats. The main types include Network Security, Data Security, Cloud Security, IoT Security, Endpoint Security, Application Security, and Zero Trust.
- Network Security: Protects computer networks from unauthorized access, intrusions, and attacks like malware, DDoS, and man-in-the-middle attacks. It relies on firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and regular monitoring to ensure data confidentiality and availability. Employee training and security audits further strengthen network resilience.
- Data Security: Focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, corruption, and breaches throughout its lifecycle. Techniques like encryption, data masking, and access control are used to mitigate threats such as ransomware and insider attacks. Regular backups and employee training are essential for maintaining data integrity.
- Cloud Security: Safeguards cloud-based infrastructures, applications, and data from threats like account hijacking and insecure APIs. It employs authentication, encryption, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to secure cloud environments. Regular audits, configuration management, and employee training ensure continuous protection.
- IoT Security: Protects Internet of Things (IoT) devices and their data from threats like unauthorized access and device misuse. Strategies include strong authentication, regular firmware updates, and secure communication protocols. Tools like IoT Device Management Platforms (DMPs) and network segmentation help enforce security policies.
- Endpoint Security: Secures devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets from malware, phishing, and device theft. Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions are used alongside antivirus software, strong passwords, and VPNs. Regular updates and employee awareness enhance endpoint protection.
- Application Security: Defends applications from threats like insecure code, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS). Secure coding practices, application security frameworks, and tools like runtime application self-protection (RASP) and web application firewalls (WAF) are employed. Regular code reviews and penetration testing help identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Zero Trust: A modern security framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It enforces strict identity verification, least privilege access, and continuous monitoring. Tools like Identity and Access Management (IAM) and micro segmentation reduce the attack surface and enhance compliance, though implementation can be complex and costly.
What are the Necessary Skills and Qualifications in Cybersecurity?
With the right skills and qualifications, you can effectively protect the information system, detect and respond to threats, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Let’s discuss the various skills and qualifications necessary to pursue a career in cybersecurity.
Top 4 Cybersecurity Skills You Must Have
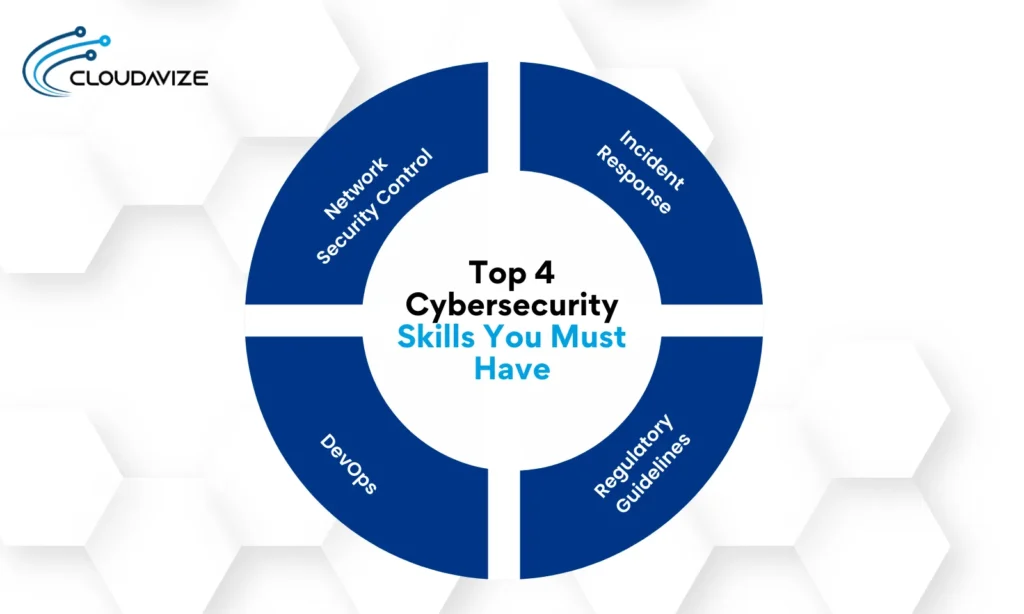
Here are the top four cybersecurity skills, ranging from technical knowledge to practical experience, you must have to land cybersecurity jobs:
- Network Security Control: Professionals must be knowledgeable about various operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS) and acquire skills in configuring, managing, and securing these OS, aligning the cloud security principles and best practices. One must also know about Intrusion detection systems (IDS), which are crucial for identifying and responding to real-time security threats.
- Incident Response: Involves identification, management, and mitigation of security incidents to minimize their impact. Cybersecurity professionals must be well-versed in structured incident response plans and the ability to analyze threat intelligence to inform response strategies.
- DevOps: Integrates development and operations teams to enhance software delivery efficiency and security. Professionals must have the scripting skills necessary for automating security tasks and managing infrastructure as code. They should be proficient in Python, PowerShell, and Bash.
- Regulatory Guidelines: Understanding and implementing security controls and frameworks such as NIST, ISO 27001, and GDPR are essential to ensure compliance with legal and industry-specific requirements. Professionals must develop and enforce policies that align with these frameworks to avoid legal penalties and protect sensitive data.
Best Cybersecurity Certifications
Obtaining cybersecurity certifications helps validate skills, enhance knowledge, and improve career prospects. Below are the best cybersecurity certifications you must have to remain up-to-date in the industry:
- Cyber Essentials Certificate: A UK government-backed certification designed to allow professionals to acquire knowledge regarding protection against cyber threats, demonstrating cybersecurity hygiene and practices.
- ISO 27001: International standard for information security management systems (ISMS) with a systematic approach to managing sensitive information and ensuring data security.
- SOC 2: A framework for managing and securing customer data based on five trust service principles: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- PCI DSS: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) sets security standards to ensure that all companies processing, storing, or transmitting credit card information maintain a secure environment to protect cardholder data and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a US federal law designed to protect sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge, ensuring the privacy and security of protected health information (PHI) for healthcare organizations.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: A voluntary framework comprising standards, guidelines, and best practices to manage and reduce cybersecurity risk, helping organizations enhance their cybersecurity posture and resilience.
Top 10 Cybersecurity Careers and Jobs
There is a growing demand for cybersecurity professionals, reflected by the significant global shortage of cybersecurity experts. A 2022 report showed an estimated gap of 3.4 million experts, and the cybersecurity workforce grew by 8.7% between 2022 and 2023, highlighting the diverse career opportunities available in the field.
Below are the top 10 cybersecurity jobs that you can land with the necessary academic qualifications and experience:
- Chief information security officer (CISO): A senior executive responsible for an organization’s information and data security. This role involves developing and implementing security policies, strategies, and programs to protect the organization’s information assets.
- Chief Security Officer (CSO): CSO is an executive responsible for an organization’s overall security, including physical security and cybersecurity. This position involves creating and maintaining a secure environment for both digital and physical assets.
- Computer forensics analysts: A professional who investigates cybercrimes by collecting, analyzing, and preserving digital evidence. Their work involves identifying perpetrators, recovering lost data, and supporting legal proceedings.
- Security engineers: These professionals design, implement, and maintain security systems to protect an organization’s information and infrastructure. They work to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
- Security architects: Security architects design and oversee the implementation of security infrastructure and policies. They ensure that security measures align with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
- Security analysts: A professional who monitors an organization’s IT environment to detect and respond to security incidents. They identify vulnerabilities, analyze threat data, and implement defensive measures.
- Security software developers: These professionals create software solutions to enhance security and protect against cyber threats. They build secure applications and tools that help organizations defend against attacks.
- Network security architects: A professional who designs and implements secure network solutions to protect an organization’s IT infrastructure. They ensure the security and integrity of network systems and data.
- Penetration testers: Professionals who simulate cyberattacks on an organization’s systems to identify vulnerabilities. They uncover security weaknesses and provide actionable recommendations for improvement.
- Threat hunters: Threat hunters proactively search for cyber threats that may have bypassed traditional security measures. They identify advanced persistent threats (APTs) and mitigate potential risks before they cause damage.
Is Cybersecurity a Good Career?
Cybersecurity is an excellent career choice due to the growing interest and increasing professional demand. With the rise in cyber threats and the critical need for protecting digital assets, there is a high demand for skilled cybersecurity experts. This field offers job security, competitive salaries, diverse opportunities, and impactful work. Considering these benefits, pursuing a career in cybersecurity is highly recommended, and investing in acquiring the necessary skills and certifications can significantly enhance career prospects.
What Cybersecurity Job Pays the Best?
Understanding the salary landscape in cybersecurity is crucial for those considering a career in this field. Salaries vary significantly based on job role, experience level, and geographic location.
- Entry-Level Jobs: Need foundational knowledge and skills in cybersecurity. It applies to recent graduates and freshers. A security analyst earns an average salary of $110,000, while a computer forensics analyst earns approximately $100,000.
- Mid-Level Jobs: Suitable for those with years of experience and a more profound knowledge of cybersecurity principles and practices. It involves performing specialized and complex tasks. A Security Engineer makes $100,000, a Security Software Developer earns $110,000, a Penetration Tester earns $122,000, and a Threat Hunter earns $140,000 annually.
- Top-Level Jobs: Senior cybersecurity positions require extensive experience and advanced expertise. These top-level roles provide strategic direction, oversee security programs, and ensure organizational resilience against cyber threats. National average annual salaries: Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) – $245,000, Chief Security Officer (CSO) – $150,000, Security Architect – $150,000, Network Security Architect – $125,000.
What are Emerging Cybersecurity Trends?
The rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity emphasizes the need for continuous adaptation to emerging threats and technological advancements. Staying updated with future trends is crucial to effectively anticipate and counteract cyber threats.
- AI: Important for enhancing threat detection, automating responses, and analyzing security data. AI algorithms identify and predict cyber threats, automate incident response, reduce threat mitigation time, and minimize human intervention.
- Data Science: Improves threat intelligence, risk assessment, and decision-making processes. Techniques like machine learning and statistical analysis predict potential cyber threats and vulnerabilities, while big data helps detect anomalies and enhance security measures.
- IoT: The proliferation of IoT devices has increased their significance in cybersecurity due to potential vulnerabilities. IoT devices pose unique security challenges, such as limited processing power, lack of standardized protocols, and a large attack surface. Emerging solutions include device authentication, encryption, and network segmentation, along with the development of regulatory standards to improve IoT security.
- CNAPP(Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms): Comprehensive security for cloud-deployed applications, integrating workload protection, vulnerability management, and compliance monitoring. Ensures continuous security through the DevSecOps pipeline and automated security policies.
- Hybrid Data Centers: Balances on-premises security benefits with cloud agility. It includes unified threat management, consistent policies, encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention (DLP). Compliance and governance frameworks meet regulatory requirements.



